1. What is Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN)?
You’ll learn:
- Why DePIN flips the traditional infrastructure model by rewarding users for real-world contributions: Think earn-to-build, not just earn-to-play.
- How projects such as Akash, Helium, and Hivemapper solve costly bottlenecks in computing, wireless, and mapping through decentralized coordination.
- What makes token incentives in DePIN more sustainable than past Web3 fads and why utility matters more than hype.
- How emerging infrastructure trends and tokenized participation are unlocking new investment and growth opportunities beyond speculative trading.
Why did we research DePIN business and why should you care?
Building a sustainable business is no walk in the park. And doing it on a Web3 infrastructure can feel more like an obstacle course.
If you’ve read our first report on modular blockchain architecture, you understand the blockchain business-specific challenges related to what we call the blockchain tetralemma.
This occurs when you try to add profitability to the usual set of concerns: decentralization, security, and scalability. But what can you do? Profitability is what a business needs, right?
So here comes DePIN—Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks—a new narrative that, if implemented properly, could compete with some of the world’s most profitable businesses. DePIN projects may eventually throw the gauntlet to Google, Amazon, or Nvidia.
In this report, you will receive an overview of how DePIN companies combine their revolutionary technological and incentivization model with the business side of their projects. Our goal is to show you different approaches, challenges, and solutions to turning DePIN into a sustainable business.
We examine some of the most successful existing DePIN projects, analyze their business models, and investigate the competitive Web3 landscape and beyond. We provide you with a thorough understanding of the possibilities and risks in various DePIN niches and concepts.
This will help you make your own involvement more beneficial. Who knows, maybe DePIN will turn out to be the killer use case the blockchain community has been waiting for over 15 years—and you’ll be part of it.
What is Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN)?
It refers to blockchain projects that incentivize users to perform a specific action that contributes to a set goal. Users receive tokens to help facilitate the bootstrapping phase of various infrastructure projects – from decentralized storage through wireless networks and shared computing to IoT.
To make this crystal clear, we’re not talking about sharing a post on social media and rewarding opportunistic people with airdrops. DePIN projects address the need to build various types of real-world infrastructure (e.g., in emerging markets).
The famous DePIN Sector Map from the Messari report illustrates how the concept works:
The Web3 world loves new narratives. And if one involves a clear investment opportunity and token incentivization at the same time, the hype is sure to follow.
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure ticks all these boxes:
- It’s a relatively new trend, even though its first serious representative – Filecoin – was introduced in 2017.
- It provides people with a huge number of new investable projects that all issue tokens as incentives.
- It allows users to earn tokens in return for an action rather than having to buy them.
The best way for you to understand DePIN’s practical side and how all this works is by looking at examples.
3 representative examples you probably know
1. Compute networks – Akash
Which problem(s) does Akash address?
Computing seems destined to become the currency of the AI age. Since before 2010, it has silently penetrated and gradually taken over our daily activities. When ChatGPT ignited an incredible outburst of AI innovation early in 2023, it finally made the headlines.
AI has made our lives more efficient, saving us time on activities that are now automated – and not only repeatable tasks. However, putting huge amounts of tasks and activity online caused an enormous increase in demand for computing to power increasingly complex AI algorithms.
Consequently, companies that provide AI solutions are now at the mercy of big suppliers such as Nvidia or Amazon Web Services (AWS). The former struggles to meet the demand; the latter’s software is centralized and pricey, and not everyone can (or wants to) afford it.
What is the Akash solution?
The Akash Network addresses both concerns. Firstly, they provide a decentralized network of computing power providers, making the AI algorithms more secure and reliable. Secondly, Akash created a kind of Airbnb for Datacenters, enabling people to lend unused computing capacity to companies and individuals in need. All this is in exchange for significant rewards.
What are some noteworthy results?
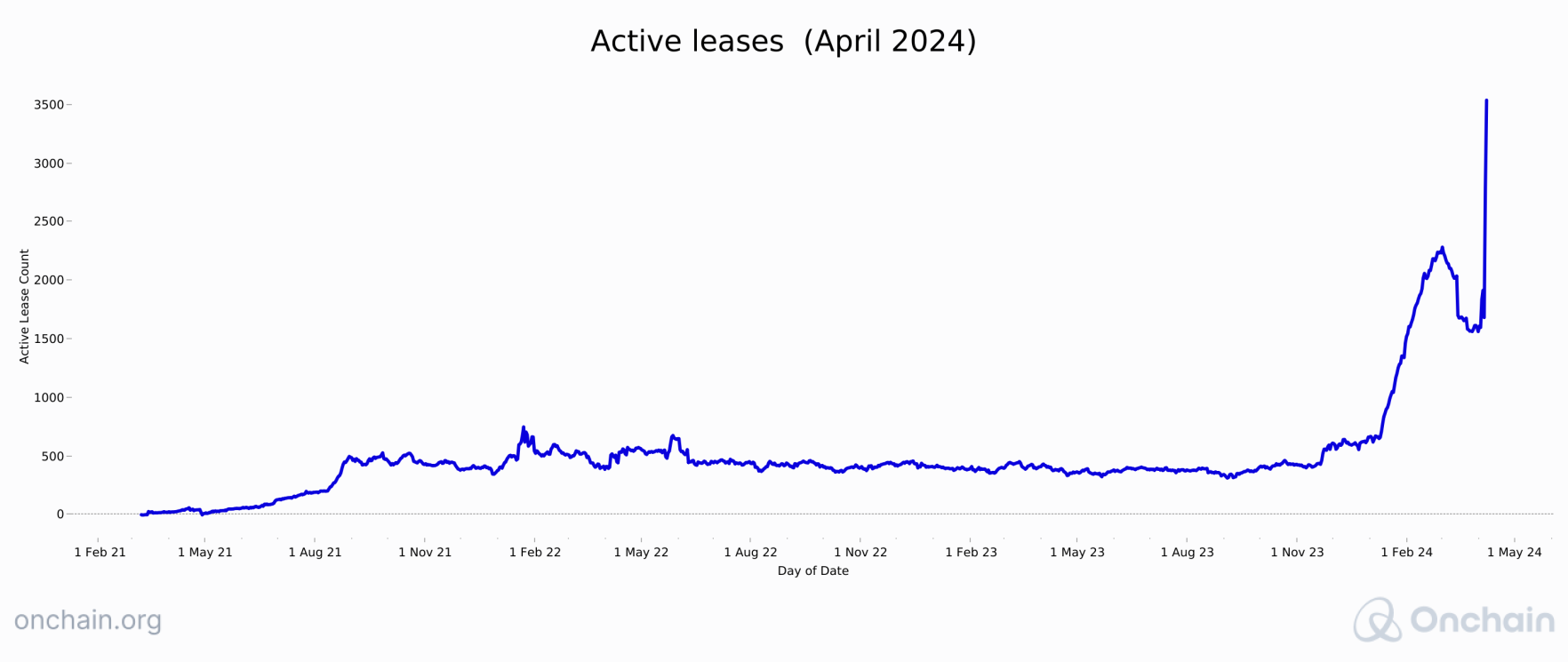
Activity on the Akash Network surged massively at the beginning of 2024, moving from 600 to over 2,200 active computing leases in a few weeks. The total is still negligible compared to AWS, which powers nearly 1.5M global businesses. However, Akash offers highly competitive prices: $5.83 per CPU on Akash compared to $32.82 on AWS. Combine this with the unique incentive model for providers and you are looking at something that may be enough to spur a significant change in the computing power market share.
2. Wireless network – Helium
Which problem(s) does Helium address?
Helium focuses on key challenges in the wireless network industry, including the need to lower data transfer costs, improve security and privacy, increase scalability, and boost innovation potential. The company also aims to mitigate economic risks such as token price volatility, network saturation, and competition from established telecommunication companies and other Web3 projects.
What are Helium solutions to industry issues:
- Lowering data transfer costs: Helium uses a proof-of-coverage consensus mechanism along with already-existing infrastructure (hotspots), avoiding the cost of establishing new infrastructure.
- Improving security and privacy: Helium’s decentralized architecture eliminates the possibility of a single point of failure and reduces susceptibility to hacking. The network relies on pseudonymized device identifiers to improve privacy.
- Increasing scalability: Unlike traditional cellular networks with constrained infrastructure capacity, the Helium Network can readily grow as more hotspots are added.
- Boosting innovation potential: Helium’s open-source design and the usage of HNT tokens encourage developers to make new devices and apps for the network, which promotes innovation.
How does Helium handle the decentralized network-specific issues?
- Token price volatility: Helium explores alternative monetization models, such as data credits for specific data transfers, to reduce reliance solely on token values and tone down fluctuation.
- Network saturation: Helium implements mechanisms to discourage excessive hotspot deployment in concentrated areas, aiming to maintain a balanced network distribution. Additionally, proof-of-coverage verification helps ensure hotspots are providing actual coverage.
- Competition: Helium targets a market niche of low-power, long-range IoT connectivity, potentially co-existing with other solutions for high-bandwidth applications. It also encourages collaboration with other networks by offering open APIs for integration.
What are some noteworthy results?
- Within barely 30 days of the launch, Helium generated remarkable traction with over 404,083 active hotspots.
- Helium raised substantial funding in its last funding round, with a post-money valuation in the range of $1B to $10B.
- The company has secured partnerships with the city government of San Jose, California, Valencia, Spain, and Dish Network for various use cases such as environmental monitoring, smart city sensors, and 5G coverage expansion.
3. Sensor networks – Hivemapper
Which problem(s) does Hivemapper address?
Hivemapper addresses several key challenges for global and local transportation and mobility management and operations:
- Increased operational costs for road planning and construction that are mostly due to the introduction of autonomous vehicles.
- Availability of reliable sources of information for governments on road maintenance.
- Lack of access to real-time data to help insurance companies solve accident-related disputes and issues.
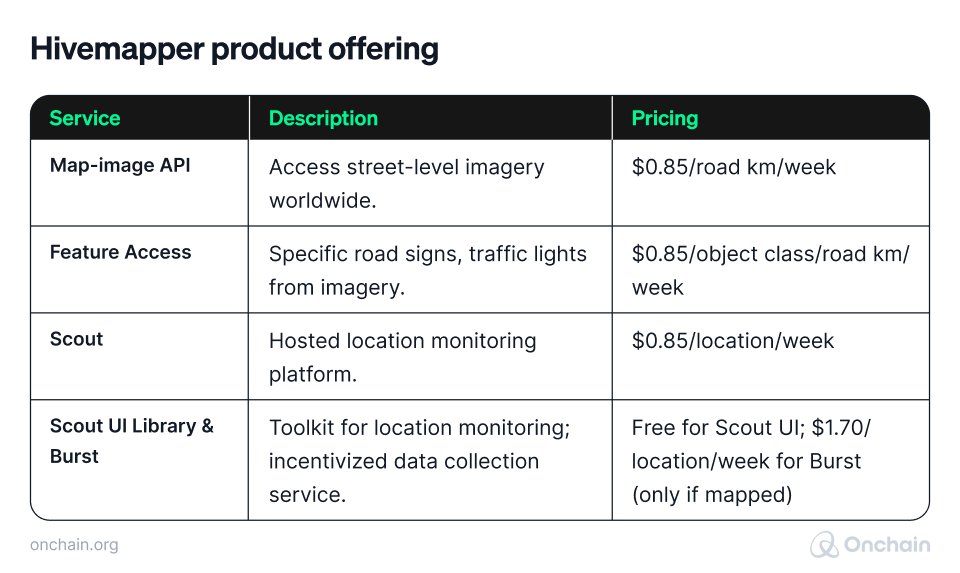
What is the Hivemapper solution?
Hivemapper’s APIs and imagery provide essential real-time traffic and mapping data.
The DePIN solution supports efficient fleet management, route planning, and package tracking through location sharing. Other sectors, such as real estate, can also benefit from the network. Hivemapper assists in property evaluation and planning, ensuring efficient land use, and ensuring regulatory compliance.