Recruiting companies use AI technology to evaluate and select suiting candidates, tracking software tracks work hours and performance of employees, and FinTech solutions are necessary to manage global payrolls.
In the race to keep up with the changing employment landscape, some qualities get lost, others are gained. With the gig economy expanding and employees frequently changing jobs, no one really knows anyone anymore. Physical distance or foreign language don’t keep people from working together.
HR managers face some challenges that standard technologies haven’t been able to solve (not even ChatGPT).
These are some of the challenges every HR professional faces:
- Lack of direct interaction with candidates and employees and ability to build trust
- Verification of employee or contractor information
- Extensive, time-consuming administrative tasks
- Long-winding cross-order payment processes
- High transaction costs
Ready for the blockparty? How blockchain can be used in HR
To understand why Blockchain and HR are a match made in heaven, you don’t need an in-depth understanding of the technology. Once you grasp what this technology brings to the table that others don’t, it’ll be obvious.

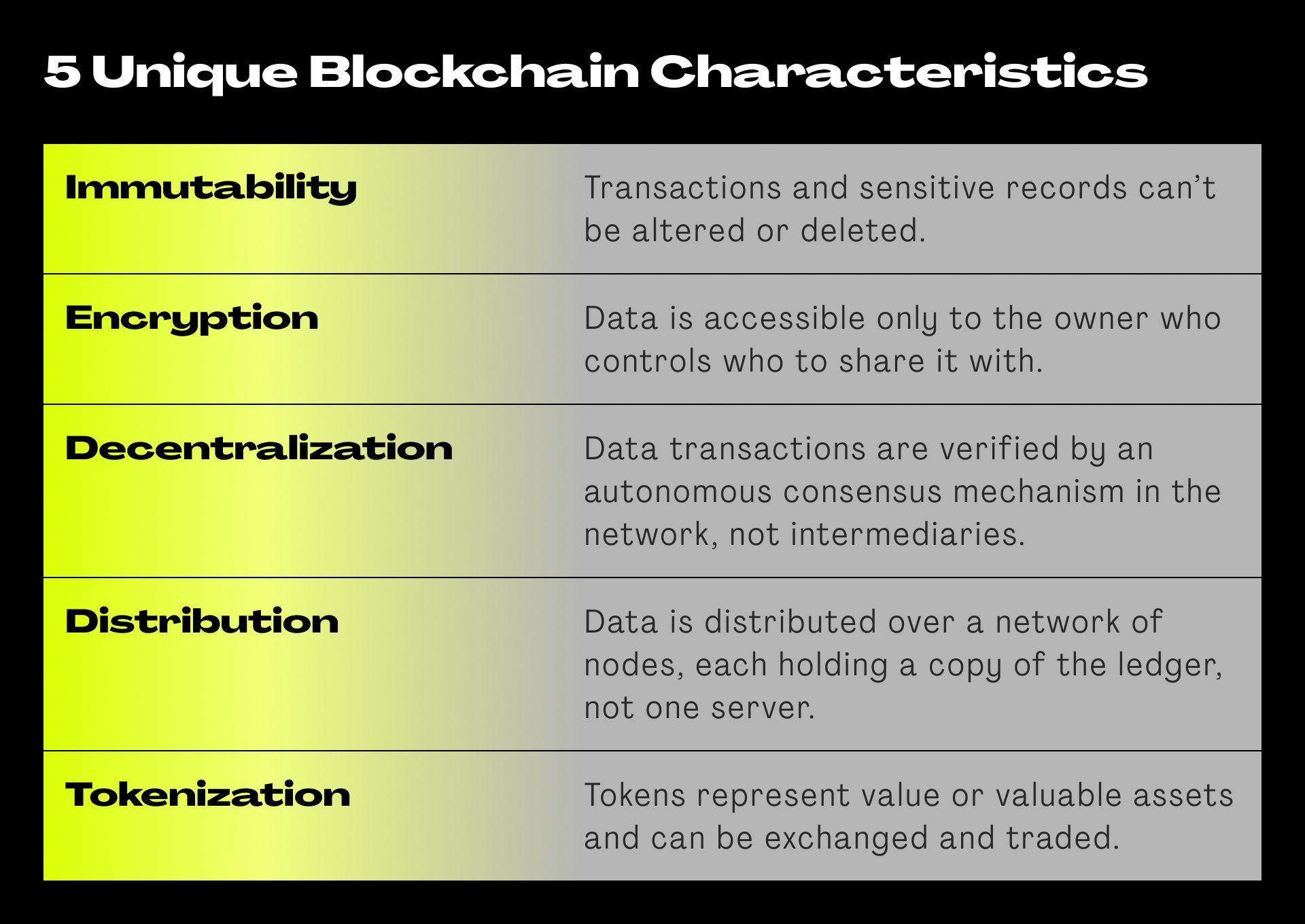
The 5 characteristics that make Blockchain unique and valuable for human resources:
- Immutability
Data stored on the blockchain can’t be altered. This makes the blockchain an excellent solution for information that doesn’t change, like someone’s date of birth or a university certificate. Data can only be added to reflect a new state, but that doesn’t impact the previous state of the data. - Encryption
Data on the blockchain is sealed by encryption and receives a time-stamp. The owner alone decides which information is visible to whom. Even though they’re part of an extensive network, they share only what’s required for a specific action. Like a candidate’s university certificate, but not their birth date. - Decentralization
Blockchain is not governed by any one entity. No one controls the network, takes administrative fees or changes the rules. The rules are programmed into the technology and the network follows them autonomously. Transactions are made directly between parties and authorized by the entire network after its legitimacy is verified. Useful, if you’re an employer in the UAE and need to pay an employee in the Philippines. - Distribution
Updated and historic blockchain data is stored on each of the network nodes (endpoints or computers). Each one has a complete, accurate record of every data exchange on the blockchain (encrypted). Fraudsters can’t change a previous data entry – like an employment record – because the network won’t approve - Tokenization
Tokenization refers to the creation of tokens. Tokens are digital representations of value. They can be used as a type of currency to be traded and exchanged for another value. For example, a reward from the employer for excellent performance. They could represent ownership of an intellectual asset like a degree or even a physical asset.
Working around the block – use cases for blockchain in HR
Let’s start with the most prevalent use case for blockchain in HR: payroll.
Blockchain opens the way to the direct exchange of value with anybody in the world. It also allows for real-time transactions with no intermediaries, such as banks. Talk about cutting transaction time and workload for both employer and employee.
Some global HR management companies, such as ADP in Japan, Papaya Global, and Deel already offer blockchain based solutions. Clients can build the most effective payroll management solutions for their operations, including blockchain-based payments.

This is most relevant if you are working with staff in different parts of the world. In remote locations, employees, freelancers or contractors may not have a bank account. In other cases, bank fees for foreign currency transactions are high. Your hiree ends up receiving significantly less than you paid and the whole deal may not be profitable.
The use of the decentralized ledger isn’t limited to transferring the blockchain-native cryptocurrency, or cryptocurrency in general. You can transfer regular currencies as well.
P2P transactions don’t require authorization from a bank or any kind of administrative procedures. Payments can even be initiated automatically when the employee completes a specific task. Temporary contracts or gig-based work arrangements become a lot simpler and smoother.
New kids on the block – blockchain in recruitment
Recruitment is one of the most resource-heavy processes in HR. The sheer number of applicants per each job opening is often overwhelming. And that’s only the beginning. What about verifying employment history, background checks and so on?

The potential of blockchain here is enormous. The immutable ledger can function as a database, storing all candidates’ credentials, certificates and employment history. When you want to hire someone, all you need is to request them to share the data. There wouldn’t be any need to fact-check or verify the information provided because forgery is out of the question.
On the other side of the deal, the applicant in a remote location can ensure that the hiring company isn’t a fake.
Biploma is a blockchain-based hosting service for academic credentials. The service works with universities and academic institutes. All diplomas and student credentials are recorded on the blockchain.
A company who wants to hire one of their graduates can verify that they are, in fact, a graduate and hold the required degree. No need to translate, notarize the diploma, no need to check against the official university records – or alternatively take the risk of hiring someone who isn’t what he says he is. This makes blockchain in talent acquisition highly useful.

And remember, no one needs to disclose information that isn’t relevant for the specific job. If a person doesn’t want to disclose their gender or marital status, the recruiter doesn’t get access to the information even though it’s stored on the chain. Just think how great that is for eliminating gender bias or other types of unconscious biases and advancing equality, diversity and inclusion.
Blockbusters – smart contracts in contract management
The technology opens completely new possibilities for contract management. This goes beyond getting rid of paperwork and bureaucracy – even though we shouldn’t underrate the value of that.
Employment has turned into a complex supply chain and the lines between employee, contractor and service provider are becoming blurry. Blockchain-based contracts can help make the convoluted mesh of contracts and contract clauses simpler to handle. But that’s not all.
You can use smart contracts to deploy bonuses or benefits automatically. Many modern companies motivate and reward their employees with performance-related bonuses. Let’s say, a sales rep is entitled to an extra percentage for every additional cold call above a certain weekly quota. And for every closed deal, they get another bonus.

You can program the smart contracts to enforce and enable the additional salary and bonus payment when the conditions are met. Many of the time-consuming and annoying tasks nobody wants to do, become automated.
Other employee benefits, such as holiday and birthday gift cards, can also be managed by smart contracts. Financial and tax obligations the employer might have towards the employee no longer require extensive administrative work. Autonomous smart contracts initiate the required action when the set conditions are met.
A condition could be a specific date in the year, or counting from the day the employee started, or a recurring interval, whatever is required.Smart contracts are even more useful when working with temporary workers, freelancers and other external service providers. IBM Garage offers blockchain-based solutions for vendor and contractor management, and AWS Blockchain provides similar solutions.
No beating around the block – blockchain for employees
Once companies embrace blockchain-based solutions, it remains to be seen how individual employees take to it. The benefits for employees in an increasingly dynamic labor market are indisputable.
It’s possible that the demand to implement the technology will come from them. Especially temporary or contract workers in locations where cryptocurrencies have a high adoption rate, might prefer to work for companies that go along with the innovation.
They won’t have to worry about getting paid on time or having to deal with bank-related bureaucracy. The immutable ledger technology grants more security.
And there’s more. Individuals have started to store their personal credentials in blockchain wallets. These wallets can include their entire personal identity, academic documents, work and training history, employee review data, and so on. The day may come when this becomes common practice among job seekers. When this happens, companies must be ready, otherwise they’ll lose out on skilled talent.
Block-solid benefits of blockchain in HR
- Trust
Remotely employing – or being employed by strangers requires people’s blind trust. But that’s not sustainable in a digitalized environment where fraud is just a ‘copy-paste’ away. The immutability of records on blockchain and the autonomous execution of certain smart contracts replace the need for interpersonal trust. - Efficiency
The adoption of a distributed ledger technology makes much of the administrative HR work redundant. Processes can be simplified and HR professionals can focus on the human aspect and skills again. - Reduce cost
Higher efficiency and removing intermediaries from HR-related processes would also reduce cost. This affects the financial side as well as recruiting, monitoring and optimizing performance and providing benefits. - Save time
Seamless transaction processing and shortened hiring procedures can lead to significant time savings. Blockchain can help speed up many of the clunky HR processes. - New value
Tokenization creates new value systems and structures. Companies can use digital tokens as an internal currency that represents any kind of value – physical, financial, intellectual, or whatever the company values. Tokens can be given as a reward for performance, a contribution to the community, or an act of loyalty. Employees could collect tokens and exchange them for another value – an item or a benefit. The sky’s the limit to the possibilities to incentivize employees using tokens.
Examples of blockchain apps for HR
Bitwage – blockchain-based cryptocurrency payroll and invoicing platform – also provides HR services – used by enterprises i.e. FedEx, YouTube, Amazon.
Chrono.tech – comprehensive blockchain-based HR software solution – mainly for Web3 professionals – includes: LaborX, a job platform connecting companies with freelancers , PaymentX for payment management, TimeX to trade and exchange cryptocurrencies.
Acorn – recently launched blockchain-based job platform for the gig economy – verifies job seeker credentials and tracks their employment history – provides a decentralized and secure way to connect job seekers with employers.
Opolis – blockchain-based payroll management, benefits management, tax compliance for independent workers – leveraging smart contracts.
Spherity – blockchain-based platform to manage employee credentials such as licenses, certifications, and training records – secure and decentralized storage for employees and employers.
Zinc – blockchain-based hiring platform simplifying and securing the recruitment process – store and verify candidate information, such as work history, references, and educational qualifications – aims to reduce fraud, save time during the hiring process, give candidates control over their data.
Datum – blockchain-based platform for securely storing and sharing personal data such as resumes, performance reviews, and other sensitive information.