What if the world ran on code instead of contracts? From tracking goods across oceans to unlocking insurance payouts without paperwork, smart contracts are quietly becoming the invisible engine behind real-world innovation.
In this article, we’ll break down how they work, where they’re making a difference, and what they mean for the future of business, from startups to global industries.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that live on the blockchain and carry out actions automatically when certain conditions are met.
Think of them as digital vending machines. If the input is right, the output happens instantly, without needing a middleman. These contracts define rules, verify terms, and enforce outcomes all on their own.
Whether facilitating payments, transferring ownership, or automating agreements, smart contracts bring transparency, efficiency, and trust to digital transactions across various industries, including finance, real estate, and beyond.
What is a blockchain smart contract definition in very simple technical terms? It’s a self-executing program.
How do smart contracts work?
Once a smart contract is created, it is deployed to a blockchain, such as Ethereum or Solana. It sits there waiting for the right triggers.
These triggers can be anything from sending crypto to checking if a shipment arrived. Once triggered, the contract executes automatically.
This simple 3-step process below puts it into a nutshell.
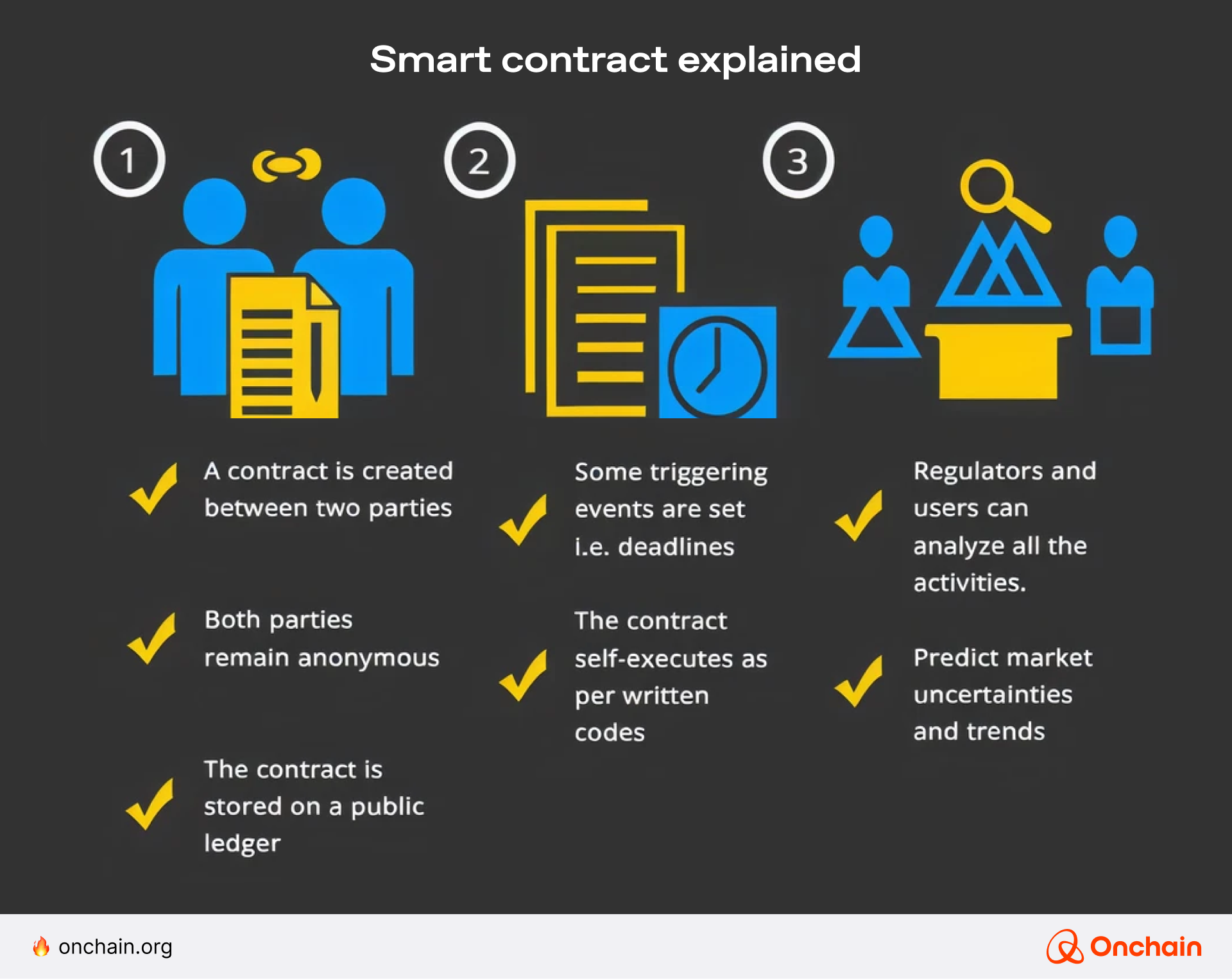
Early smart contract use cases include initial coin offerings (ICOs), where funds were released only if funding goals were met. Today, smart contracts form the backbone of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, Non fungible token (NFT) marketplaces, and decentralized autonomous (DAO) platforms.
Smart contract use cases in finance and DeFi
The application of smart contracts is streamlining everything from legal documents to real estate, yet they really took off in the world of decentralized finance (DeFi).
By automating everything from lending and borrowing to trading and staking, smart contracts are having a major impact on the finance world. Here are some of the key use cases.
- Lending: Protocols like Aave utilize smart contracts to enable users to deposit crypto and earn interest, or borrow against collateral, all without the need for a bank.
- Insurance: Smart insurance contracts can trigger automatic payouts when conditions are met (e.g., flight delay or weather events).
- Derivatives: Platforms like Synthetix use smart contracts to manage synthetic assets, tracking the value of real-world commodities or currencies.
Imagine removing the need for banks, brokers, or middlemen — smart contracts make that possible by replacing trust with code.

Supply chain management and smart contracts
To put it in no-nonsense terms: in supply chains, smart contracts act as digital truth-keepers.
Each step of a product’s journey from factory to warehouse to store can be tracked and verified using the blockchain.
Smart contracts automatically trigger payments when goods reach their destination or alert stakeholders if something goes off track.
For example, a coffee exporter can use smart contracts to verify bean quality, track shipments in real time, and get paid instantly when the buyer confirms delivery.
It’s like giving your entire supply chain a smart nervous system.

Smart contracts in real estate
If you have ever been involved in buying property, you’ll know it is full of paperwork, bureaucracy, and slow-moving intermediaries.
Smart contracts can simplify this.
They can automate escrow, handle title transfers, and ensure funds are only released once all terms and conditions are met.
A good example in a real estate deal is where a smart contract could release payment only once both parties have digitally signed the agreement, title documents have been verified, and all inspections have been passed.

Smart contracts in energy trading
Smart contracts are also powering peer-to-peer energy marketplaces, allowing households with solar panels to automatically sell excess electricity to neighbors.
Platforms like Power Ledger and WePower use smart contracts to facilitate transparent, real-time energy trading without any middlemen required.
This not only optimizes energy use but also opens up new income streams for individuals in decentralized energy networks.
Smart contracts in gaming and digital assets
In Web3 gaming, smart contracts manage in-game economies, asset ownership, and reward distribution without relying on centralized servers.
Gamers can truly own their assets, such as weapons, skins, or land, and trade them freely on marketplaces, thanks to smart contracts ensuring transparency and scarcity.
Projects like Axie Infinity and Illuvium showcase how smart contracts can create new play-to-earn models and community-driven ecosystems.
The role of smart contracts in digital identity verification
Identity verification can be a time-consuming and manual process, particularly in banking, government, and healthcare sectors. Another area where smart contracts come to the rescue.
They simplify this by automating identity checks securely on the blockchain.
Users can control their personal data and share only what is needed, thereby reducing the risk of fraud or data leaks.
For instance, instead of repeatedly uploading ID documents, a user could share access to a blockchain-verified identity, such as a digital passport that institutions can instantly verify without storing sensitive information.
Using a smart contract is faster, safer, and puts control back in the user’s hands.
Smart contracts in NFTs
NFTs are more than just digital art; they’re programmable assets. And smart contracts are what make them so powerful.
One widespread and popular use case for smart contracts that benefits NFTs is royalty enforcement.
Artists and creators can set smart contracts to automatically receive a percentage every time their NFT is resold, without relying on third parties or chasing down payments.
It’s simple and innovative. The NFT creators get paid easily and forever.
Healthcare and smart contracts
Smart contracts in healthcare are tackling data inefficiencies and cutting admin costs. They automate patient consent, process insurance claims, and enable secure, permission-based data sharing.
A good case in point here could be a patient switching doctors or even moving cities, as their records would be transferred instantly after access is approved. This would save time, reduce the bureaucracy, and eliminate the never-ending paperwork headaches.
Of course, challenges remain, such as regulatory clarity and tech adoption. Nevertheless, the potential is clear.
A future outlook: The potential of smart contracts across industries
Smart contracts are powerful, but they’re not magic. Adoption still faces real-world challenges, including scalability, legal recognition, and the need for user-friendly interfaces.
That said, progress is moving fast. Developers are building smarter, more flexible smart contract platforms.
Legal frameworks are catching up. And with AI, we’re even seeing the rise of self-adjusting Tokenomics 2.0 models that respond to market dynamics in real time.
The real-world adoption of smart contracts is just getting started. And as businesses from logistics to law firms begin to plug into blockchain, the use cases will continue to grow.
We developed a cutting-edge and well-researched report into the next generation of Web3 infrastructure. It offers case studies, landmark metrics, and the precise steps for investors and founders to get involved in real-world assets. These comprehensive sector reports are typically delivered only to our members, but you get to access it as a part of the RWA lesson flow. Next, you’ll be introduced to the report so you can nerd out and build your own real-world asset plan.



