Binance Smart Chain is known for having high throughput, the chain uses a Proof of Staked Authority consensus. BSC is EVM-compatible and offers very low fees. The chain is also very much focused on ecosystem growth, supported by Binance and its massive treasury.
The Future Is Modular

Key takeaways
- We predict that the combination of the Ethereum blockchain and Layer 2 solutions will be the preferred option for both users and people willing to build Web3 projects.
- This tandem has the potential to solve the two critical struggles Layer 1s are facing: the lack of network effects and the inability to solve the blockchain trilemma (or tetralemma, as stated in the report).
- The speed of app development, and the growing interest of VCs, indicate a bright future for Layer 2s in general. And the higher the network effects in this category, the fewer resources for alternative Layer 1s to compete with Ethereum.
- Layer 2s appear to improve the business model of blockchains as well. As of now, basically, no Layer 1 except for Ethereum is and can become profitable. The introduction of, and app development on Layer 2s can finally increase the popularity of non-speculative revenue streams in Web3. We explore the example of friend.tech and Base L2, and also the general financial condition of all major Layer 2s.
- It’s important to bear in mind that Layer 2s still face significant challenges, including a high level of centralization, problems with UX, or still constrained scalability. However, as they’re much better conceptualized and designed than Layer 1s coming from earlier stages of blockchain development, they can successfully address these struggles in the near future.
The current state of Layer 1s
The crypto industry is still in its early development stage. Despite its young age, blockchain infrastructure already has a history of critical events and significant changes:
Fourteen years after Satoshi Nakamoto’s famous whitepaper brought cryptocurrency to life, nearly all the major blockchains that caused a significant technology alteration are still around. The pioneer currencies, Bitcoin and Ethereum, which were at least in part created out of ideology, continue to play a major role in the crypto space. However, the introduction of alternative Layer 1 blockchains – ignited by Lisk, Neo, and Waves and continued by EOS, Fantom, Avalanche, Cardano, or Solana – marks the beginning of a different and fascinating period in the technical development of the crypto industry. Their development was motivated by the desire to replace, improve, or even “kill” Ethereum as the leading L1 blockchain.
Competition is a strong driver of innovation. The first Ethereum challenger entered the crypto ring eight years ago, and to this day, no one has come close to achieving Ethereum’s market cap (~$244B) or the level of adoption.
The table below shows how various blockchains intended to take on Ethereum.
How alternative L1s planned to challenge Ethereum?
$ 34.7 B
market cap
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
$ 25.7 B
market cap
Challenges Ethereum by having high throughput, low transaction costs, and fast processing speed, It leverages a Proof of History consensus combined with PoS for efficient and scalable blockchain performance.
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
$ 13.5 B
market cap
Offering a more scalable, energy-efficient, and secure blockchain platform through its Ouroboros PoS algorithm and a focus on research-driven development.
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
$ 7.7 B
market cap
Offering higher transaction throughput, rapid finality, and lower fees. Using the Avalanche Consensus Protocol consensus allows for a more scalable and customizable blockchain creation (thanks to subnets).
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
$ 6.7 B
market cap
Focusing on providing interoperability within its ecosystem as well as a higher level of independence for chains connected to its mainchain.
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
$ 3.5 B
market cap
Using Tendermint's consensus algorithm, and IBC to communicate interoperable between the different blockchains in the network. It’s designed to scale horizontally and leave as much independence to its app-specific blockchains as possible.
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
Ethereum keeps running high, but naturally is not without issues. Its blockchain struggles with scalability, users lament the slow transaction speed and very high costs. In fact, the costs are incomparable with both other Layer 1s and non-blockchain solutions. Moreover, after the transition to PoS (Proof of Stake) consensus, concerns over Ethereum’s real decentralization are becoming loud.
Does this mean, as blockchain users and builders, who are forced to rely on Layer 1s, are we facing a tragic conflict? Before we answer this, let’s dig deeper into the two main struggles Layer 1s are up against in 2023 and beyond. In this first part of our report, we will provide you with a thorough understanding of the intricacies of the challenges, how they interact and affect each other, and what we can conclude from this analysis.
Ethereum’s task at hand is to solve the blockchain trilemma.
Alternative Layer 1s need to generate and benefit from network effects.
What is the blockchain trilemma, and why is it unsolvable?
Blockchain networks are designed with specific goals and priorities. The various design choices are based on the intended use cases of the specific blockchain project and typically involve trade-offs.
The concept of the scalability trilemma was formed in response to the challenges faced by different blockchain projects when trying to balance between: decentralization, security, and scalability.
The trilemma claims that blockchain systems can only have at most two of the following three properties:
Scalability
As blockchains inevitably grow, they need to handle an increasing number of transactions and users without sacrificing performance. A scalable blockchain is designed to process a higher throughput of transactions efficiently
Security
Data and network security are crucial for the integrity of a blockchain network. It involves protection against various attacks, such as double-spending or unauthorized changes to the blockchain. A secure blockchain ensures the integrity and immutability of the data it stores.
Decentralization
The concept of decentralization is in the heart of blockchain technology. Distribution of control and decision-making across a network of participants eliminates the need for a central authority.
You cannot achieve higher scalability without compromising on security and decentralization. To improve security, you need to inhibit scalability, and to maintain full decentralization you restrict scalability.
This need for trade-offs hinders the widespread adoption of blockchain technology and has held back the growth and adoption of basically all the Layer 1 blockchains. For example, Ethereum struggles the most with the “scalability” aspect. As a result, transactions processed through this blockchain are much slower and more expensive than on other, less secure, and less decentralized Layer 1s. You can find the TPS (Transaction per Second) for major Layer 1s in the following chart.
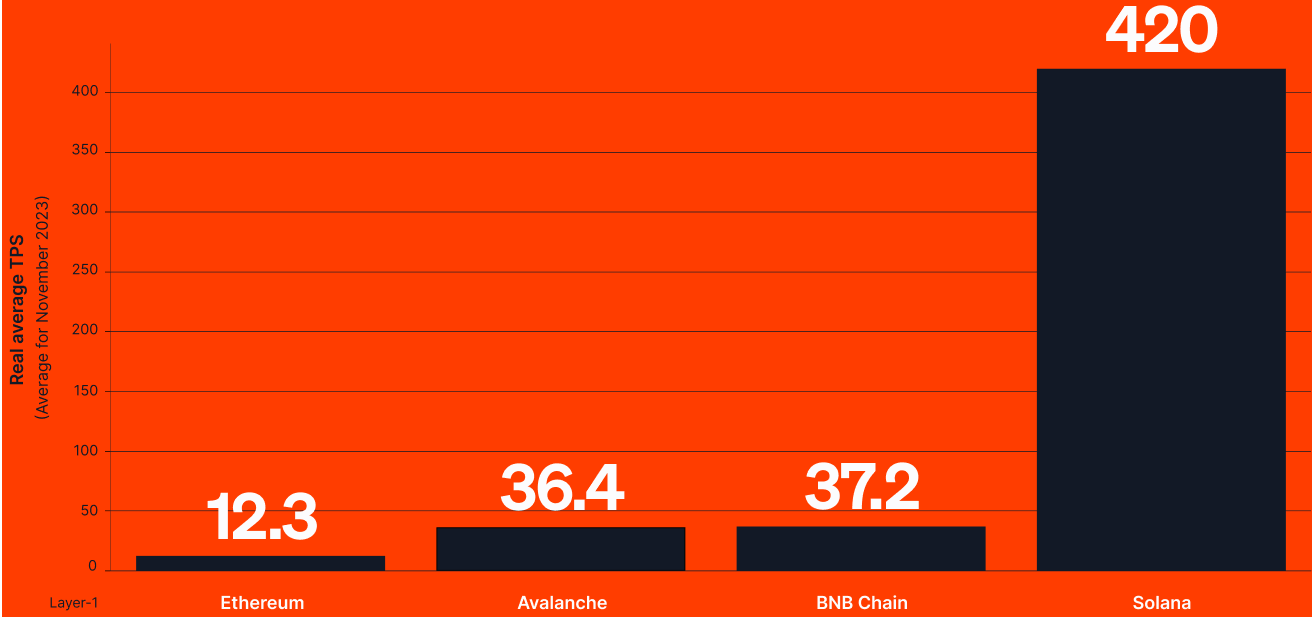
Source: Dune Analytics (@k06a, @robin_y)
However, let’s put Ethereum aside and look at how these numbers compare to the average 1,500-2,000 transactions per second conducted by payment processor VISA. Or a maximum of 65,000 TPS that it can arguably handle. None of the numbers compete.
Moreover, the TPS numbers (as well as TVL) are often inflated and sometimes generated and boosted by internal microtransactions. A good example is Solana, where approximately 80% of transactions are made up of its own consensus messages. We analyzed the real average TPS based on actual charts, not declarations made by protocols. Let’s add another metric that highlights the scalability issues of all blockchains: swaps per second (conceptualized by consumer insights agency Dragonfly Capital). This metric applies to the factual transactions made by Layer 1 users, rather than internal transfers between validators. You can find more on this methodology in a recent article by CoinTelegraph and a comparison of swaps per speed in the table below.
Source: Dragonfly Capital
Again, when we compare these numbers to VISA as a benchmark for discussing Layer 1s’ speeds, we see that these scalability issues are not limited to Ethereum anymore. Also, not only TPS should be improved – especially because boosting it “no matter what” can impede scalability – but from a user point of view the cost of blockchain operations is even more crucial.
Consequently, we need to add one more element to the blockchain trilemma, turning it into a “tetralemma” (“tetra”, from Greek, meaning “four”). Scalability, decentralization, and security issues affect also the business aspects of running a blockchain, leaving us with the question of whether Ethereum (or any other Layer 1) can maintain these 3 important traits, and be profitable (the fourth part) at the same time.
Exploring the blockchain tetralemma
The typical business model of a blockchain is clear: selling block space in exchange for fees. The more block space is sold, the more money gets poured into the protocol. And, as blockchains remain decentralized protocols, these assets are redistributed to network participants or burned to reduce the inflation of the token representing a particular chain.
However, the blockchain trilemma discussion shows that the most decentralized chains also face the highest risk of being unscalable. Ethereum, the biggest one in terms of transactions, TVL (Total Value Locked), and generated revenues is a perfect example.
Ethereum leads the way in terms of network effects for both users and developers. They benefit from the vast ecosystem of apps and the variety of options but, at the same time, struggle with high fees and low throughput. In short, the more activity, the higher the fees.
To illustrate this point, here are some numbers:
1.03
The average gas price in November 2023 (based on Etherescan
2.99
The more realistic median price for 2023
13.88
In times of higher congestion, i.e. May 2023, the daily median was as high as $13.88.
30
During times of a bull market, i.e. in 2021, the median price per transaction exceeded $30.
Why Layer 1s are lacking business sustainability
Assuming Ethereum may be compromised by its own inefficient infrastructure, why don’t we see alternative Layer 1s as a valuable option from a business perspective? The short answer is: Layer 1 blockchains practically can’t become profitable.
Ethereum continues to dominate the revenue and earning categories among Layer 1s, despite the challenges. Besides TRON, the main blockchain for USDT which generates most of its revenue from stablecoin transactions, no Layer 1 comes close to Ethereum when we discuss business.
Following is a revenue comparison chart.
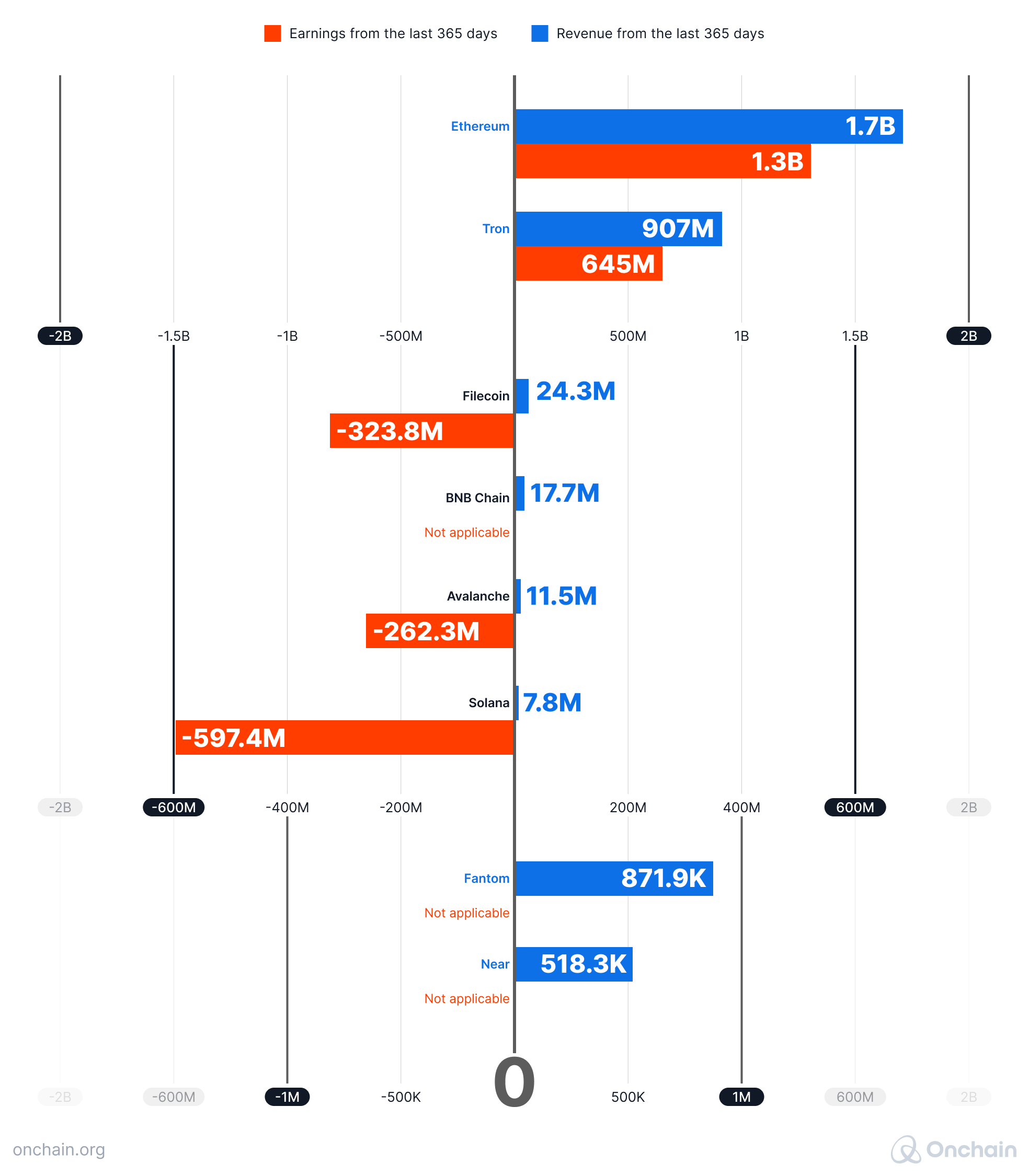
A comparison of the revenues and earning across the major L1s
The numbers speak for themselves. Ethereum’s revenue is twice as high as that of the second in line, TRON, while the third achieves less than 2% of Ethereum’s revenue with negative earnings.
Moreover, we don’t know what the real costs of maintaining the companies and foundations behind these protocols are. Even a part of $1.3B earnings that is captured by Ethereum’s Foundation should be enough to pay salaries for their members as well as cover costs related to grants and other incentives. Their latest financial statement is from April 2022 and states $48M of spendings in 2021. Even if this number increases in the future – which can be expected – Ethereum still remains profitable, when investigated like any traditional company; in fact, very profitable. This can’t be said about many other Layer 1s.
And there is more to consider besides the pure revenues of the protocol. In the sections below, we analyze the number of dApps built per blockchain. One figure stands out among the crowd: 5,071 applications created on BNB. The number tops even Ethereum’s impressive 4,385. However, when we compare the revenues generated by dApps built on these blockchains, Ethereum has a clear upper hand, no matter what blockchain we’d pick for comparison.
Moreover, despite the higher number of unique active wallets (542.4M on BNB vs. 146.8M on Ethereum) and the general number of transactions (1.44B vs. 0.19M), BNB is far from Ethereum’s earnings.
Behind the numbers
The main explanation for these numbers is rooted in the aforementioned business model of blockchains. Alternative Layer 1s sell their blockspace at a price that is too low for them to become profitable in the long term.
Fees are so small that these chains need to either
- raise the incentives for the network participants, which increases the inflation and general costs for the protocol, or
- raise the fees to generate more earnings.
What if they got rid of any of their substantial attributes like low costs and high throughput?
Even in the current state, these advantages are not enough to provide alternative Layer 1s with a competitive advantage in the battle over user acquisition against Ethereum. Despite a significant number of transactions and very inviting costs, nearly all Layer 1s are lacking adoption and interest compared to the more expensive and allegedly non-scalable Ethereum.
The only exception is BNB. On the downside, this blockchain is more centralized than the others described, which brings us back to the trilemma and the question of the tetralemma.
Can a blockchain become sustainable without compromising scalability and centralization at all?
Before we provide you with a data-driven answer, we need to explore the second major struggle of blockchains – this time mainly for alternative Layer 1s: network effects.
The power of network effects and why they matter in Web3
In general, network effects occur when the value of a platform increases (often exponentially) due to the growing number of users. Two well-known non-Web3 examples are:
- Uber – the more drivers are available on the app, the more convenient it becomes for passengers and vice versa, less drivers means less convenience
- Airbnb – the more hosts offer their rooms on the app, the more attractive it becomes for guests and vice versa, less hosts means less opportunities and choice
Based on this schema, networks with more users become exponentially more valuable than their competitors.
The network effects were first introduced on a larger scale with Metcalfe’s Law, but restricted to telecommunications. His idea turned out to be applicable in every industry that relies on a two-sided market.
Network effects - telecommunication example
How network effects impact Web3
- Web3 is specifically dependent on network effects:
- They enable a higher speed of development in its still infancy stage.
- They provide an essential utility for dApps.
- They help to make blockchains secure and decentralized.
- They lead to the creation of diverse and vibrant ecosystems.
- They enable community growth and, in consequence, its support (in both protocols’ marketing and development).
Contrary to the blockchain trilemma, with which all Layer 1s struggle, the network effects are particularly troublesome for the Ethereum competition, meaning all Layer 1s except Ethereum. The following table includes figures that highlight this conclusion.
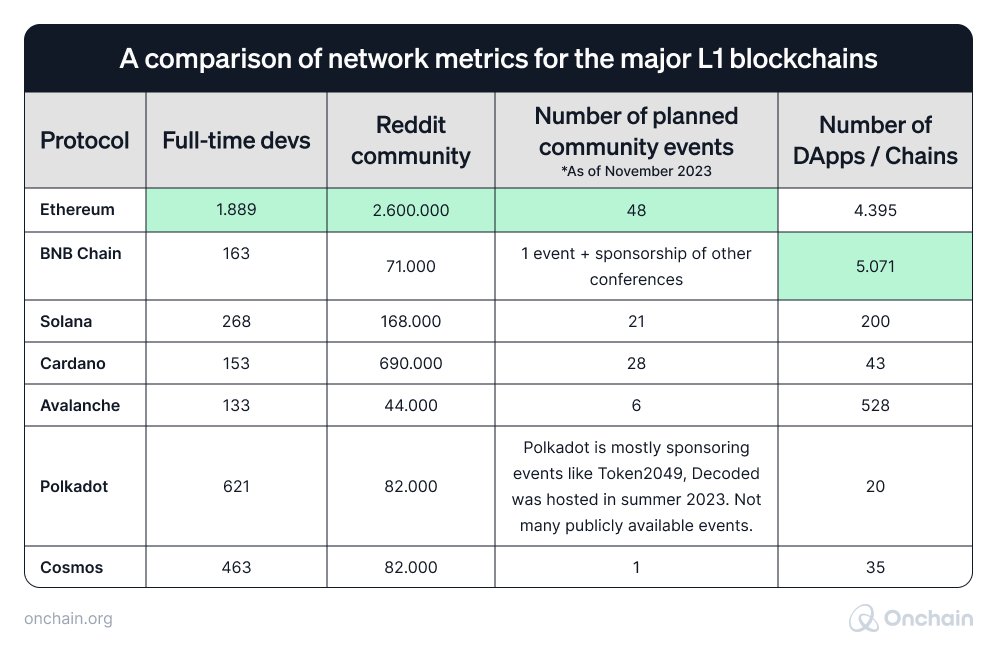
Sources: Developer Report, DappRadar, L1s’ websites, and social media accounts
The number of full-time developers and the general size of the community help Ethereum capitalize on Metcalfe’s Law and thereby increase its network effects. It’s especially important regarding the speed of development of high-quality dApps. More developers mean more innovation, a broader range of applications, and quicker problem-solving.
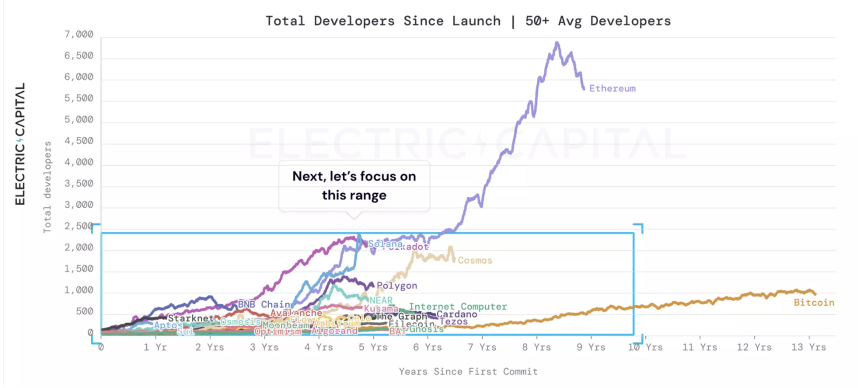
Source: Electric Capital
The above graph shows the extent to which the number of developers functions as a catalyst for the Ethereum ecosystem growth. We must also keep in mind that the overall number of Web3 developers in the world is still limited and inhibits the progress potential of other Layer 1s.
Here is an overview of the primary network-effect-related challenges Layer 1s faced in 2023.
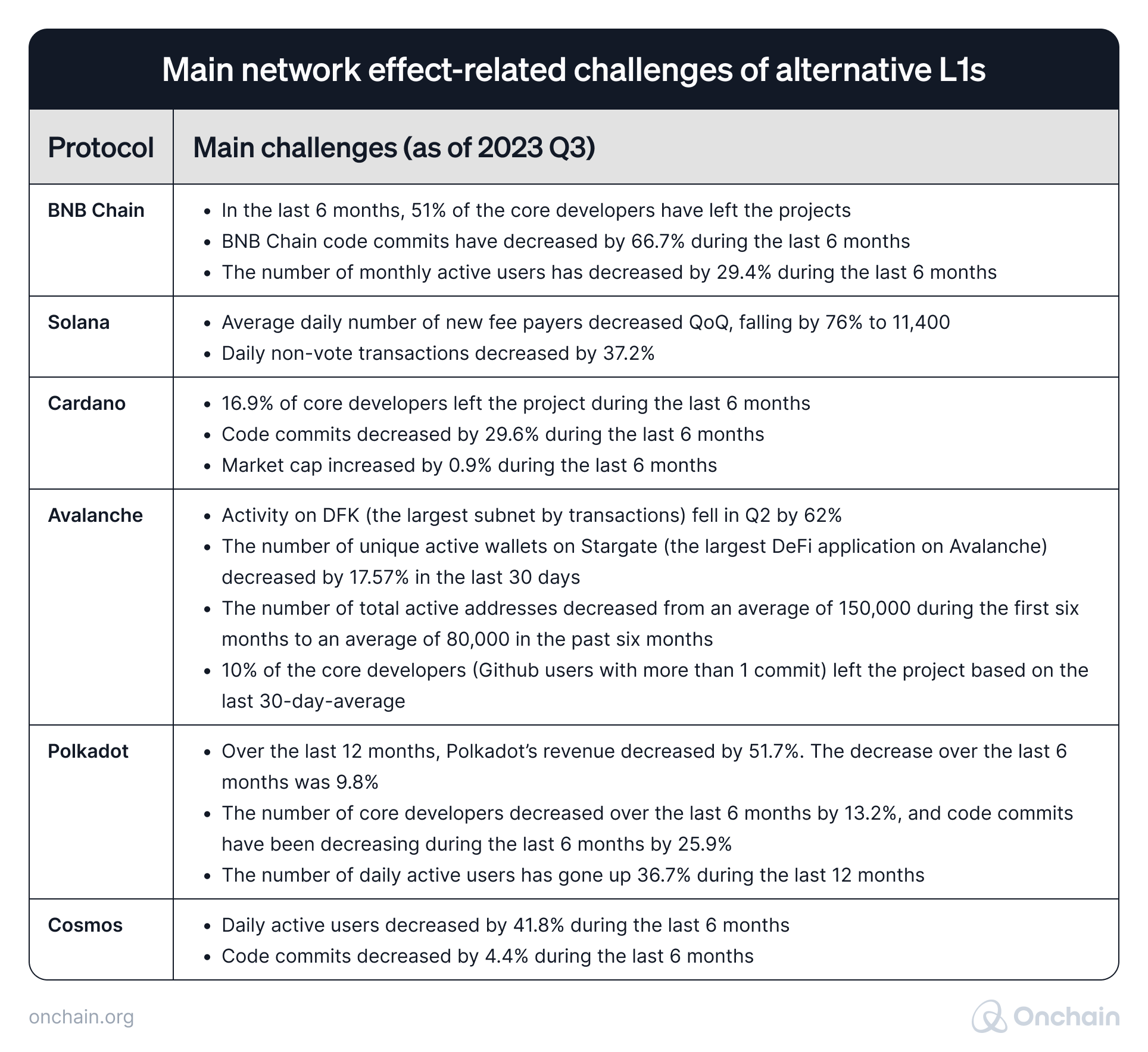
Sources: Messari, DappRadar, TokenTerminal
Network champion Ethereum
Developers and users are one aspect of network effects, but not the only players in the field. Based on our research, entrepreneurs and projects willing to build in Web3 most frequently look for:
- Smart contracts support
- Access to the user base
- Grant funding available
Ethereum can provide all three elements on a much larger scale than any other blockchain operating in the space – either directly or through its ecosystem projects.
In comparison, Ethereum also significantly lowers the entry barriers to the blockchain industry and facilitates a smoother start based on:
- Potential partnerships
- Visibility of the project
- Higher level of base security
Additional factors contributing to Ethereum’s massive network effects
- Widespread adoption of standards – Ethereum introduced standards like ERC-20 and ERC-721, which have become widely adopted across the industry.
- Dominance in DeFi and NFTs – making Ethereum the primary ecosystem not only for developers but most importantly, for individuals.
- High liquidity and trading volume – improving the user experience of the ecosystem and holding on to users despite the struggles with the blockchain trilemma/tetralemma.
- Recognized brand and trust – after the last bull run of 2021-2022, it is hard for anyone to imagine the future of blockchain without Ethereum. The protocol established itself as the foundation of the industry and maintained its status, despite the massive growth of its competitors during this period. The network continues to attract more developers and users.
These network effects become most obvious to an individual when looking at the number of dApps built on Ethereum and other ecosystems. The graph below compares pure TVL (Total Value Locked) in various applications. As you can see, Ethereum dominates across all timeframes, with a 60-75% market share maintained over the last 2 years.
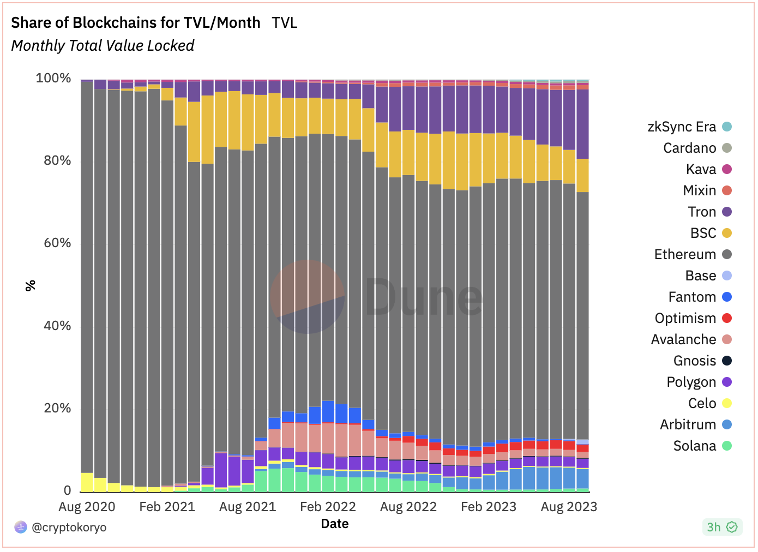
Source: Dune Analytics (@cryptokoryo)
These findings are backed by the general activity in dApps. The below displayed table shows that, compared to the BNB chain, Ethereum counts a lower number of unique wallets and applications built. On the other hand, the value generated from these apps and their NFT volume are remarkably higher on Ethereum. We can assume that it’s the only Layer 1 where dApps and users interacting with them are genuinely active and not artificially inflated.
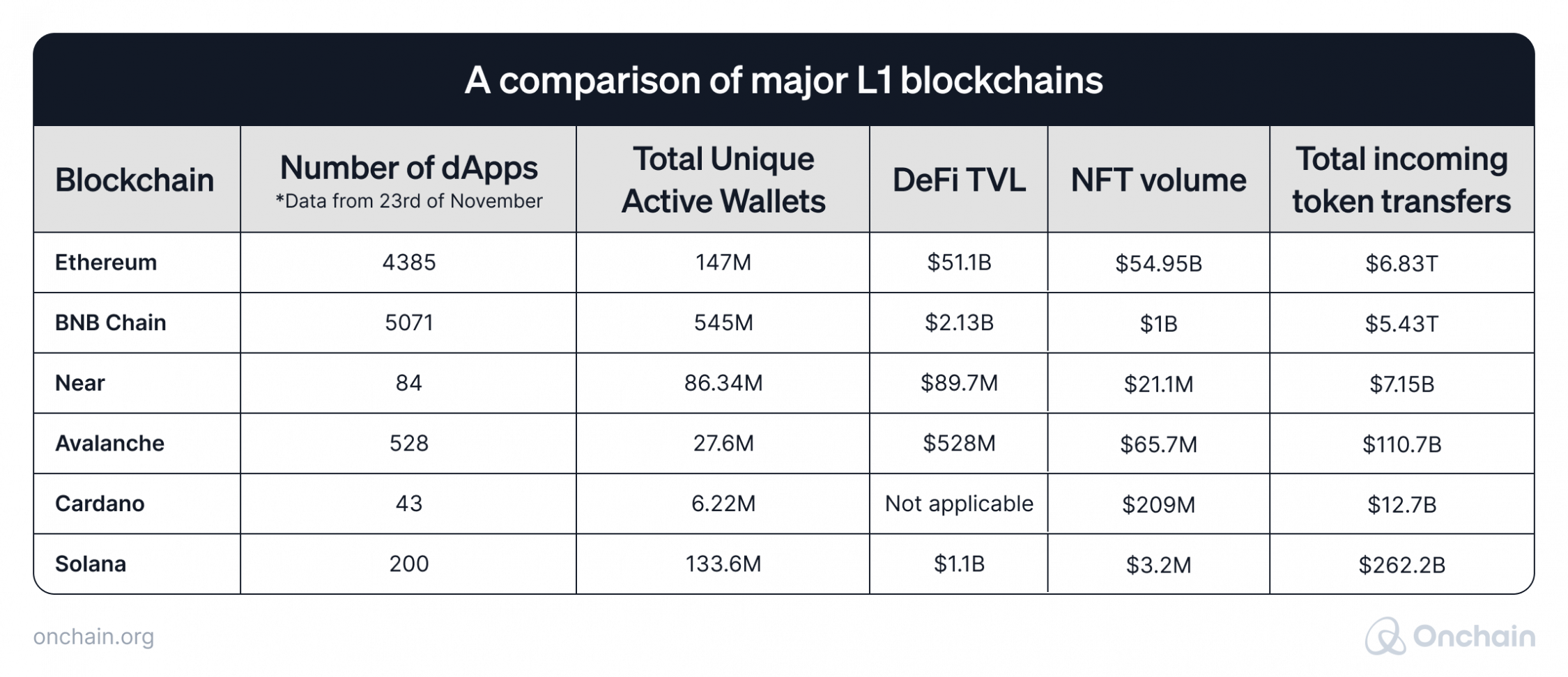
Source: DappRadar
Note that the numbers above refer only to the Ethereum Mainnet. If we added its scaling solutions (more on that in the following sections), such as Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync, or Base, the results would look as shown in the following table:

Source: DappRadar
Ethereum’s dominant position becomes even more evident when we look at individual categories of Web3 projects. It leads across the board DEXs, NFTs and RWAs.
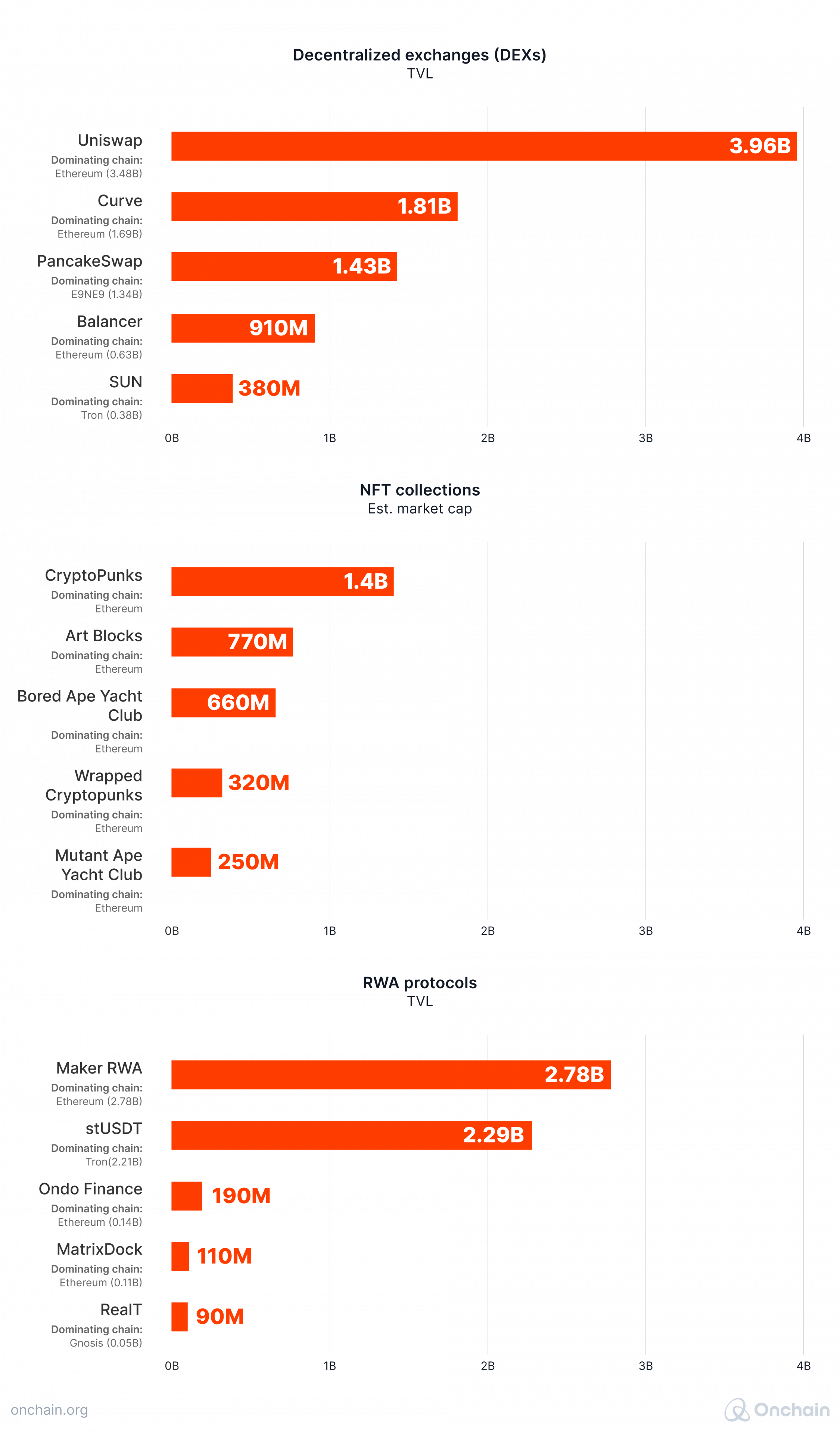
Sources: DefiLlama, CoinMarketCap
To sum it up, these factors lead to the conclusion that Ethereum spearheads the Layer 1 landscape:
- sustainability and potential profitability of the protocol
- network effects within the ecosystem
- dominance in the DeFi and NFT areas
- over 60% of the market’s total value is locked in the protocol
One critical question remains: Are they enough to ensure long-term success, if Ethereum doesn’t solve its scalability issues?
In the second part of this paper, we will focus on technological advancements aimed at tackling the major struggles of Layer 1s laid out in the first section. We examine if they can solve the blockchain tetralemma while capitalizing on existing network effects, which would bring the much awaited technical Web3 readiness for mass adoption.
Achieving scalability through layers
In general, there are two main ways in which Layer 1s can scale to increase the throughput and reduce general costs for both the protocol and users.
Layer 1 scaling
Layer 1 scaling requires upgrades to the protocol.
It can include strategies, such as:
- Increasing block size
- Reducing block time
- Improving the consensus algorithm
- Compressing the onchain data
- Introducing parallel processing
- Sharding (that emerged in the past as the most promising onchain scaling solution and was expected to scale the Ethereum blockchain)
However, Layer 1 scaling faces significant challenges, such as:
- decentralization and security concerns
- limitations in the consensus algorithm
- lacking consensus within the community
- limited innovativeness compared to offchain scaling
- These caused developers and entrepreneurs to explore the second option of modular
- scaling (mostly in the form of Layer 2s) in more depth.
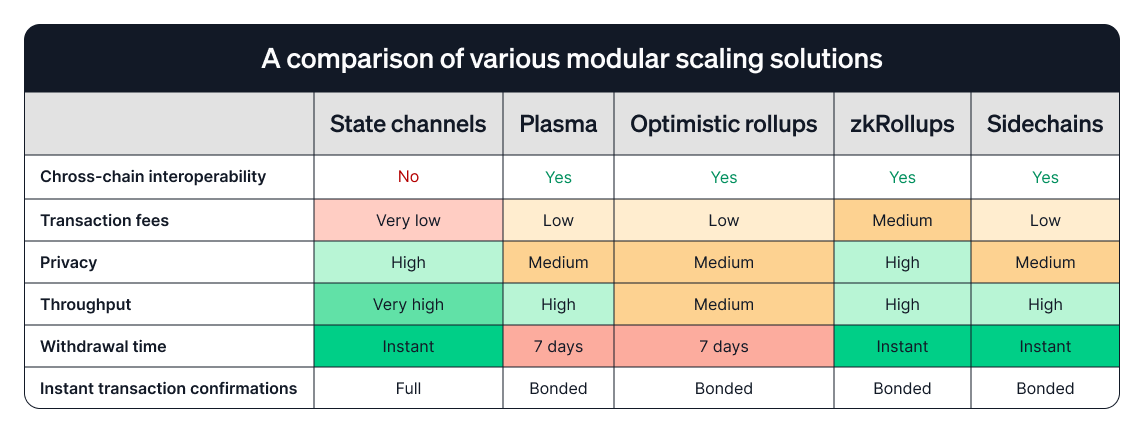
Modular scaling
The advantage of modular scaling lies in the fact that it isn’t implemented on the Layer 1 and doesn’t require any changes to the existing protocol.
So-called Layer 2 solutions that derive their security directly from the Layer 1 consensus are currently the most popular modular scaling developments. Examples include optimistic rollups, and zero-knowledge rollups.
The idea behind Layer 2s is to scale by processing transactions outside the Layer 1 blockchain network while leveraging its strong decentralized security.
With this in mind, it’s not surprising that the vast majority of Layer 2 projects so far decided to build on Ethereum. They can directly address the blockchain’s biggest challenges, and benefit from its network effects and developer activity.
What are the main modular scaling types?
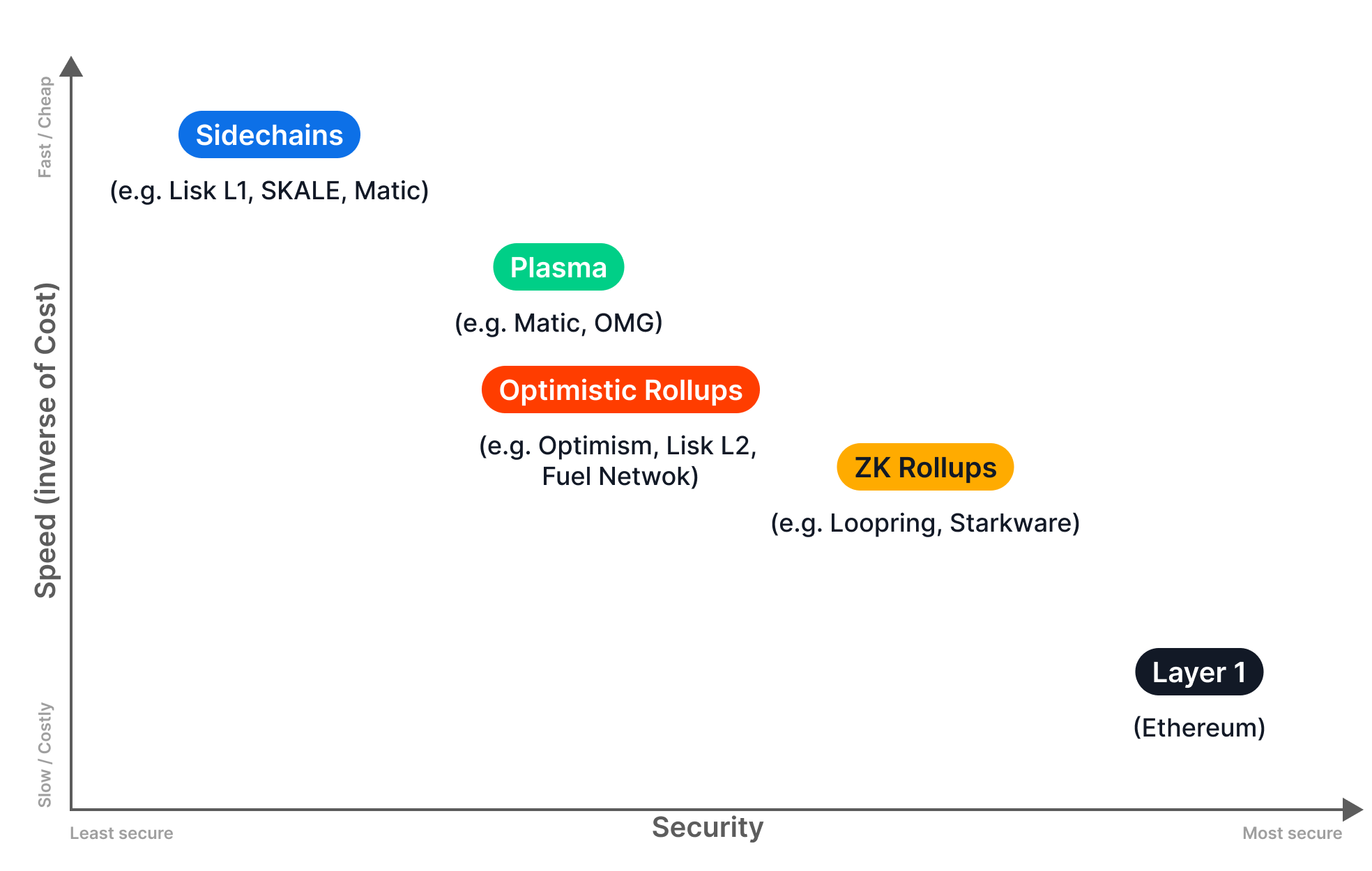
Source: Medium (@Clear Chain Capital)
Rollups
Rollups process transactions outside the Layer 1 and only post aggregated data to the Layer 1. Because all transaction data is included on a Layer 1, rollups benefit from the inherent security of it, most notably of Ethereum.
There are two main categories of rollups, each with its own security approach:
- Optimistic rollups operate under the assumption that transactions are valid by default and only execute a verification as a response to a dispute (Arbitrum, Optimism, Base).
- Zero-knowledge rollups execute computation off-chain and provide validity proofs to the blockchain (zkSync, zkEVM).
Rollups are the most prevalent type of modular scaling, with 8/10 biggest scaling solutions relying on this technology.
Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains that run alongside the Layer 1. They connect to the Layer 1 through bi-directional bridges and operate under their own consensus rules and block parameters.
Sidechains allow for more experimental or application-specific environments while staying linked to the Layer 1.
The most popular examples are Lisk, Cosmos, and Polygon with its PoS Ethereum sidechain.
State channels
State channels use multi-signature contracts, allowing participants to conduct transactions off-chain swiftly and without restrictions, settling the final state on the Layer 1. This approach reduces network congestion, fees, and delays.
This concept allows multiple transactions to occur in a private channel located off-chain. Only the initial and final states are recorded onchain. This is ideal for applications requiring high transaction throughput, like gaming or microtransactions.
State channels are a complex solution that still suffers from many flaws. After years of development the technology is still in the testing phase. In addition, the UX leaves much to be desired for.
Plasma chains
Plasma chains are distinct blockchains tethered to the main Ethereum blockchain, utilizing fraud proofs (similar to optimistic rollups) for resolving disputes.
The created child-blockchains are anchored to the main Ethereum blockchain. Each child-chain can have its own rules and operate independently, which is beneficial for creating scalable decentralized applications (dApps).
Source: MatterLabs
The potential of Layer 2 blockchains
Layer 2s could play a crucial role in shaping the future of Ethereum, an ecosystem that grabs the majority of network effects in Web3 but struggles to scale. At the same time, they could also be essential for other chains in building their ecosystems.
The reasons are: Layer 2s
- enhance Ethereum’s scalability, enabling it to support a larger number of transactions
- enable a significant reduction in gas fees
- lead to notably faster transactions than on Ethereum Layer 1
- leverage the security of Ethereum (although their security model is typically less battle-tested than Ethereum’s and leads to many concerns –
- explained in more detail in the following sections)
- benefit from Ethereum’s ecosystem of developers, dApps, and users, leveraging its vast network effects
Additionally, the introduction of Layer 2s, especially in the form of rollups, has dramatically simplified the creation of dApps and enables interoperability as a basis for entire ecosystems. This is due to the fact that basically the same tools as in Ethereum are used. This eliminates the learning time for programmers and makes it easier for entrepreneurs to find developers to support their project.
L2s were developed to alleviate the scaling challenges that can make deploying and transacting on Ethereum cost prohibitive and slow. Optimism’s first blockchain, OP Mainnet, was built by Ethereum developers for Ethereum developers; EVM equivalence means builders on OP Mainnet don’t need to learn any new code or skills to leverage the speed and cost benefits provided by the L2. Teams across the Optimism Collective are active in the broader Ethereum community through numerous initiatives including core development. – Smit Vachhani, Partnerships at OP Labs.
In the following table, you can compare the most important Layer 2 rollups and their characteristics.
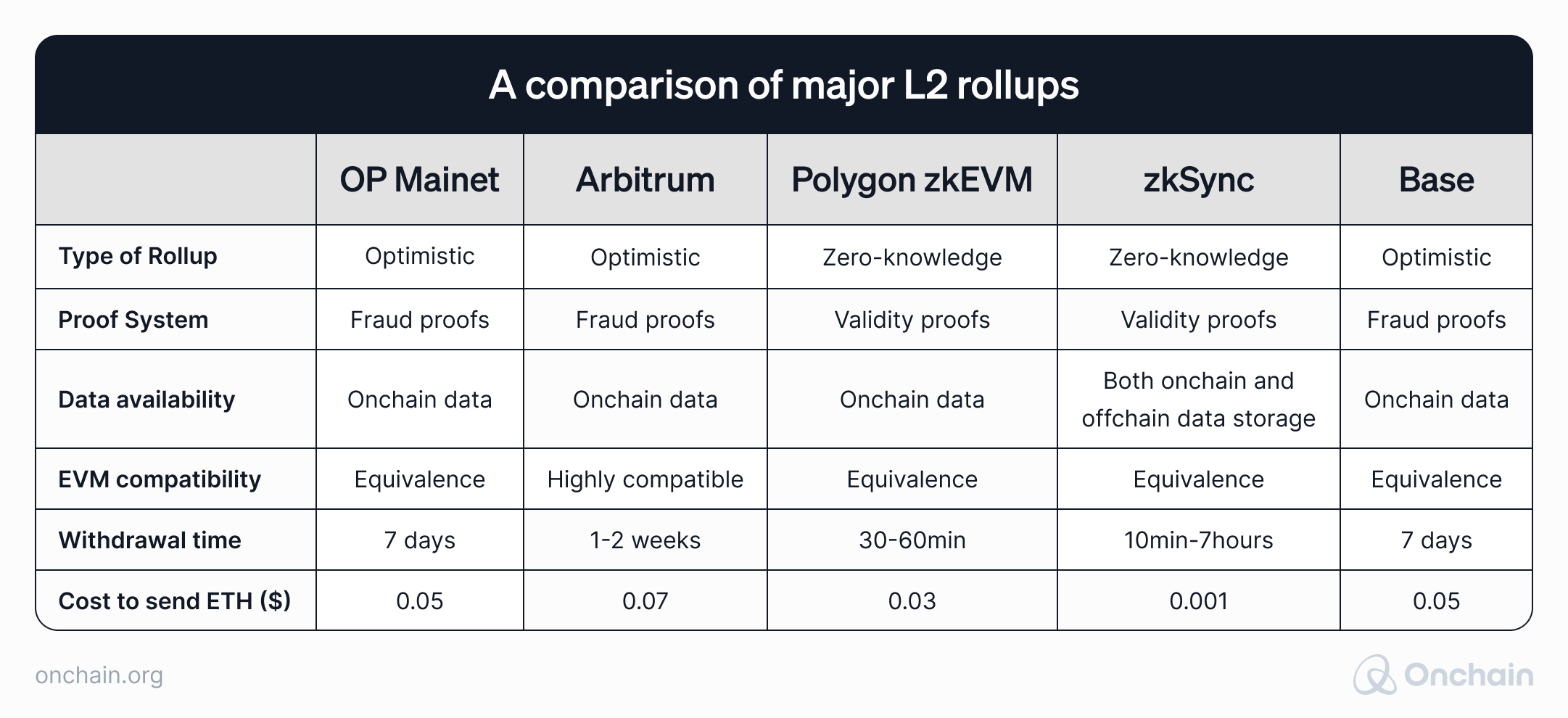
Sources: L2Beat, individual analysis
Rollup-as-a-Service is another important advancement that helps going beyond creating individual Web3 projects. Entrepreneurs can establish entire ecosystems of relatively independent and interconnected applications.
What is Rollup-as-a-Service?
Rollup-as-a-service (RaaS) refers to a service that provides infrastructure, tools, or support for projects wanting to implement rollup solutions without having to build the entire stack themselves.
RaaS providers enable developers and entrepreneurs to build independent Layer 2s on Ethereum. By doing so, they gain more freedom to customize their environment to their specific needs and achieve better scalability allowing them to build their own ecosystem.
The solution includes features ranging from developer tooling, shared sequencers, or no-code deployments. Compared to existing Layer 1 or Layer 2 platforms, this could potentially provide enhanced scalability, transaction speeds, or better fee structures.
In addition to greater flexibility, other RaaS benefits are:
- Sustainability: If a developer chooses to design their own customized rollup, then they can capture the settlement fees and design a sustainable business model for their project.
- Isolated fee market: Due to a separate rollup, there is no battle for transaction execution. The result is an overall improvement in the user experience.
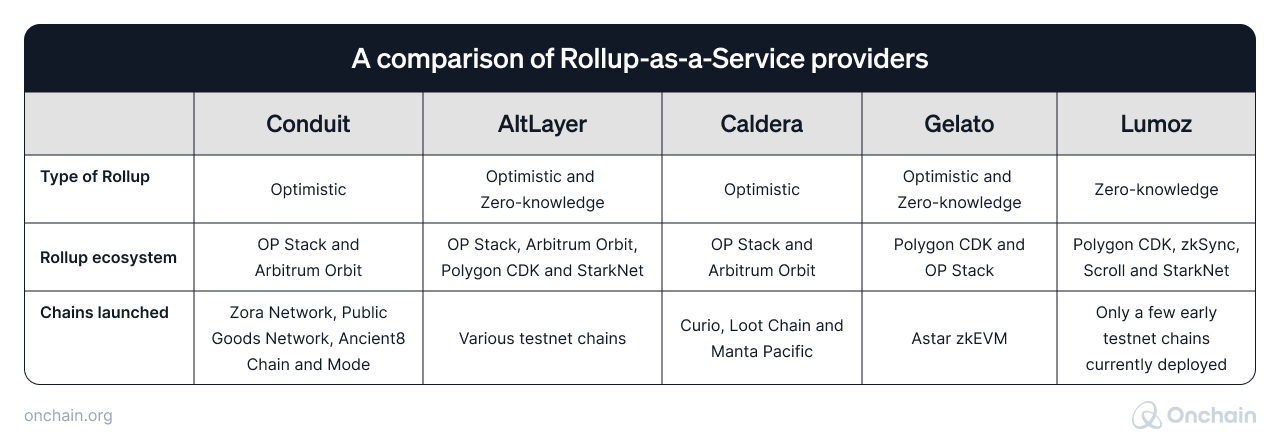
Sources: Messari, Binance Research
No gain without pain for Layer 2s
Based on these arguments, it seems like building dApps on Layer 2s or running your own rollup is a no-brainer for both Web3 developers and entrepreneurs. But let’s not jump to conclusions before we see the whole picture.
Layer 2s are still in the early development stage. And despite their complexity and the possibility of relying on already existing solutions (e.g., Ethereum for security), they face their own blockchain trilemmas, tetralemmas, and other minor struggles.
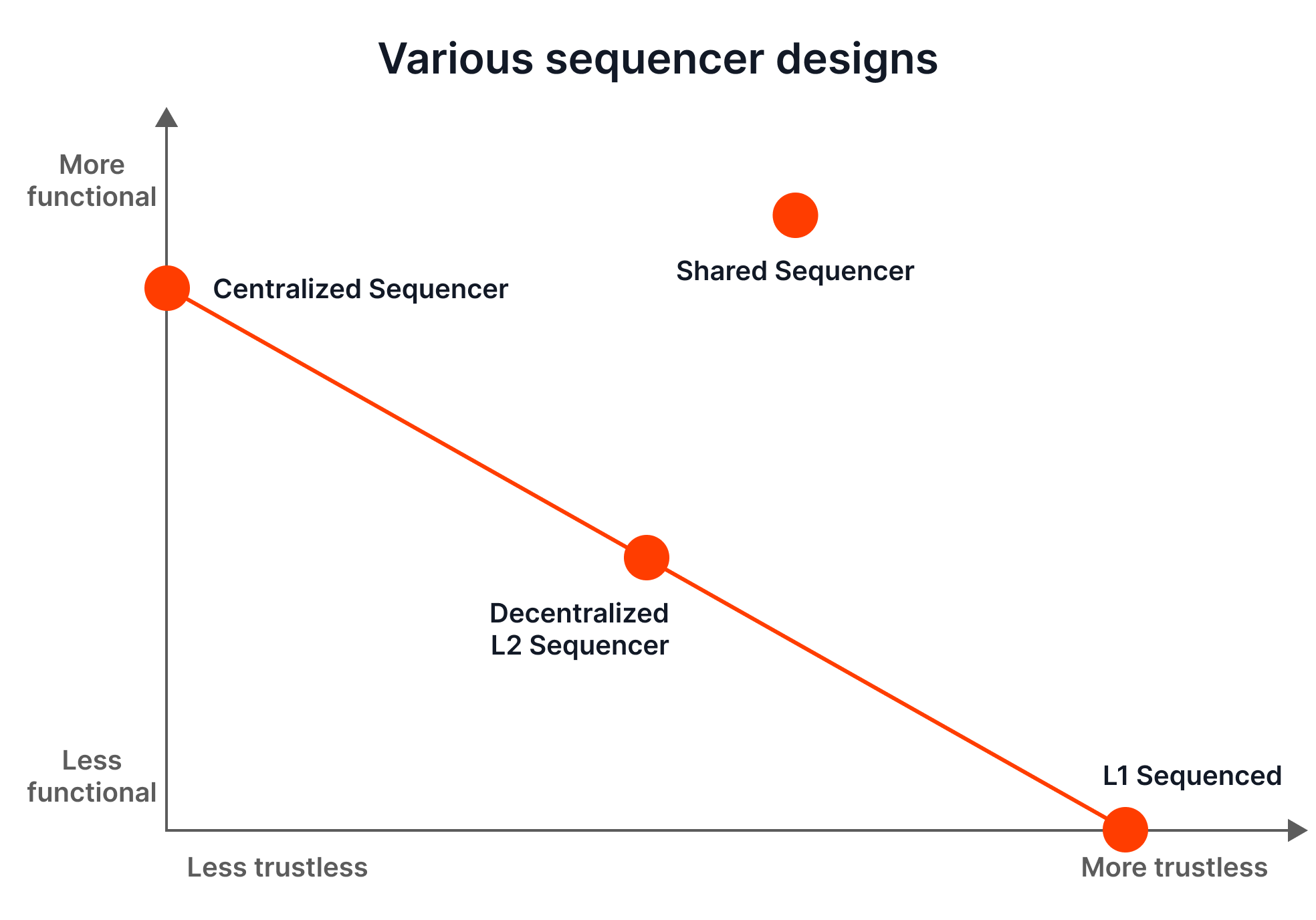
Source: John Char Bonneau
ONE
Centralization concerns
ONE
Centralization concerns
Sequencers play a pivotal role in the Layer 2 architecture. They are responsible for ordering and batching transactions before they are finalized on the Layer 1. Currently, nearly all existing sequencers are owned by their respective chains. This may result in a single point of failure if any attack happens on the sequencers.
TWO
Security / Governance
TWO
Security / Governance
Layer 2 solutions do not have effective governance models in place to ensure that they are developed and managed in a transparent, democratic, and open way. This is particularly important for decentralized Layer 2 solutions without a central authority or owner.
THREE
Layer 2 interoperability
THREE
Layer 2 interoperability
Currently, there are no easy-to-use solutions to transfer assets between different Layer 2 chains. A user might have to revert to Layer 1 bridging to transfer assets and therefore pay higher fees.
FOUR
Data availability
FOUR
Data availability
For modular blockchains like Layer 2 rollups, the data availability is more complex, requiring extra verification procedures. Various articles propose solutions to this problem. (E.g., Implementing rollups over Ethereum data shards).
FIVE
User experience
FIVE
User experience
Although Layer 2 provides faster transaction processing, token withdrawal is still not seamless in solutions like optimistic rollups which currently still dominate the market. These require a 7-day lock-up before withdrawing tokens back to Layer 1. There are some attempts to improve on this issue.
SIX
Scaling in development
SIX
Scaling in development
The main advantage point of Layer 2s – the ability to scale Ethereum – is arguably not impactful enough at the moment. When we look at the TPS and average fees comparison below, it is clear that performance of Layer 2s in their current state is not sufficient to facilitate mass blockchain adoption just yet.
Daily TPS and average swap fees for L2s
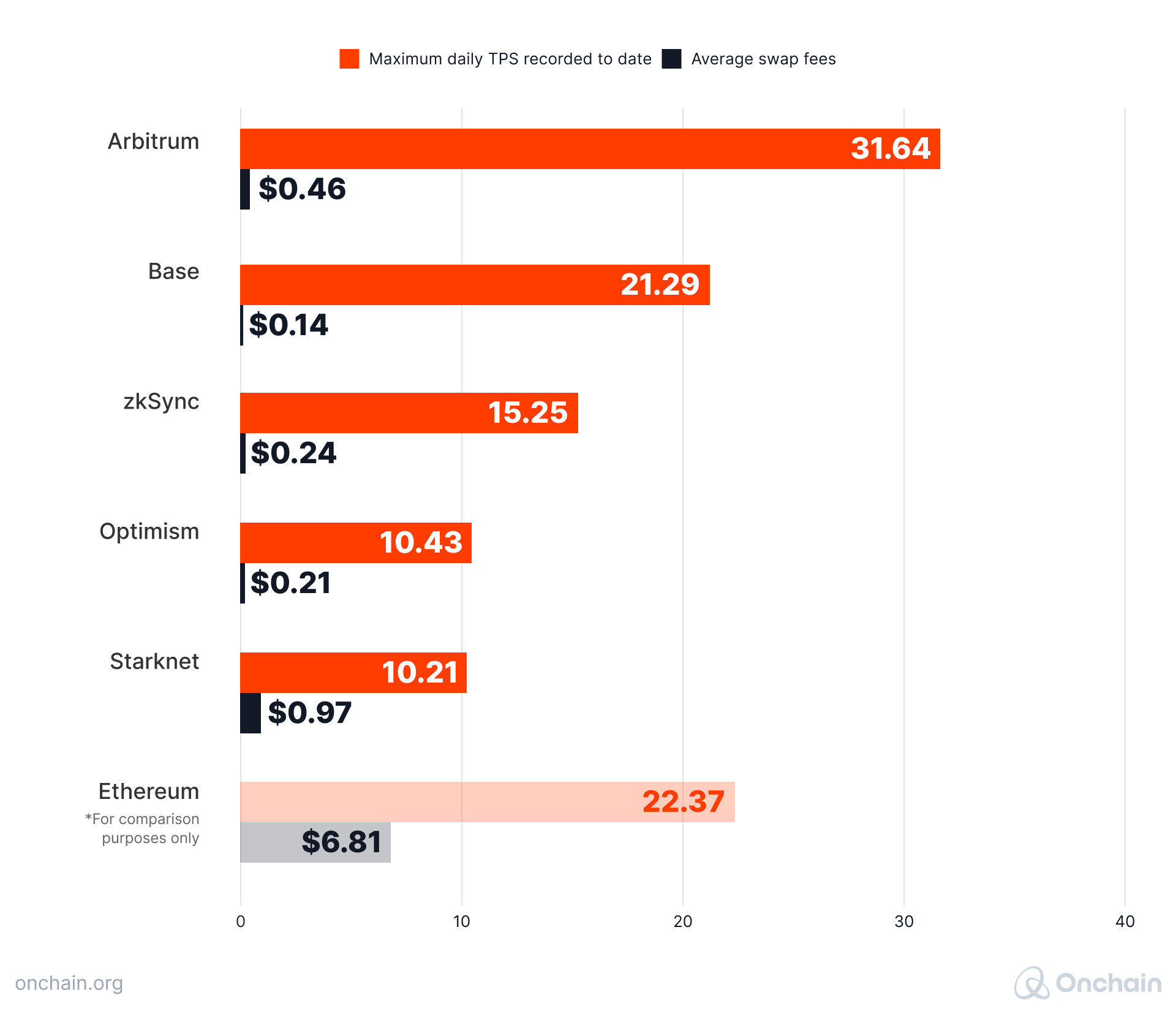
Sources: L2BEAT, L2Fees, Dune Analytics (@msilb7)
On the upside, there are a lot of technical breakthroughs around the corner and we expect a drastic change in 2024 and beyond.
Market trends for Layer 1s and Layer 2s
In the following section, we’ll evaluate how much the RaaS providers and the general features of Layer 2s practically appeal to both new-coming and existing Web3 projects.
Note that this analysis includes only projects that publicly stated their connection with Layer 2s (by transitioning into a Layer 2, building on Layer 2, or just considering such activity). Most likely, there are many more protocols and individual apps ready to utilize or simply test Layer 2 technology.
We decided to analyze the market moves on 3 primary levels:
- Layer 1s that decided to become Layer 2s in the near future, leaving their history as “alternative Layer 1s” behind.
- Companies and Web3 projects that decided to launch their Layer 2 blockchains (instead of Layer 1s) for various reasons.
- Projects that decided to build on Layer 2s instead of building on Layer 1s or along with Layer 1 versions of their apps.
1. Alternative Layer 1s transforming into Layer 2
Moving from being a Layer 1 blockchain to becoming a Layer 2, costs a lot of financial and other resources. Despite this, we’ve already seen projects taking this bold decision.
Below are five blockchains taking this step and their reasoning behind the decision.
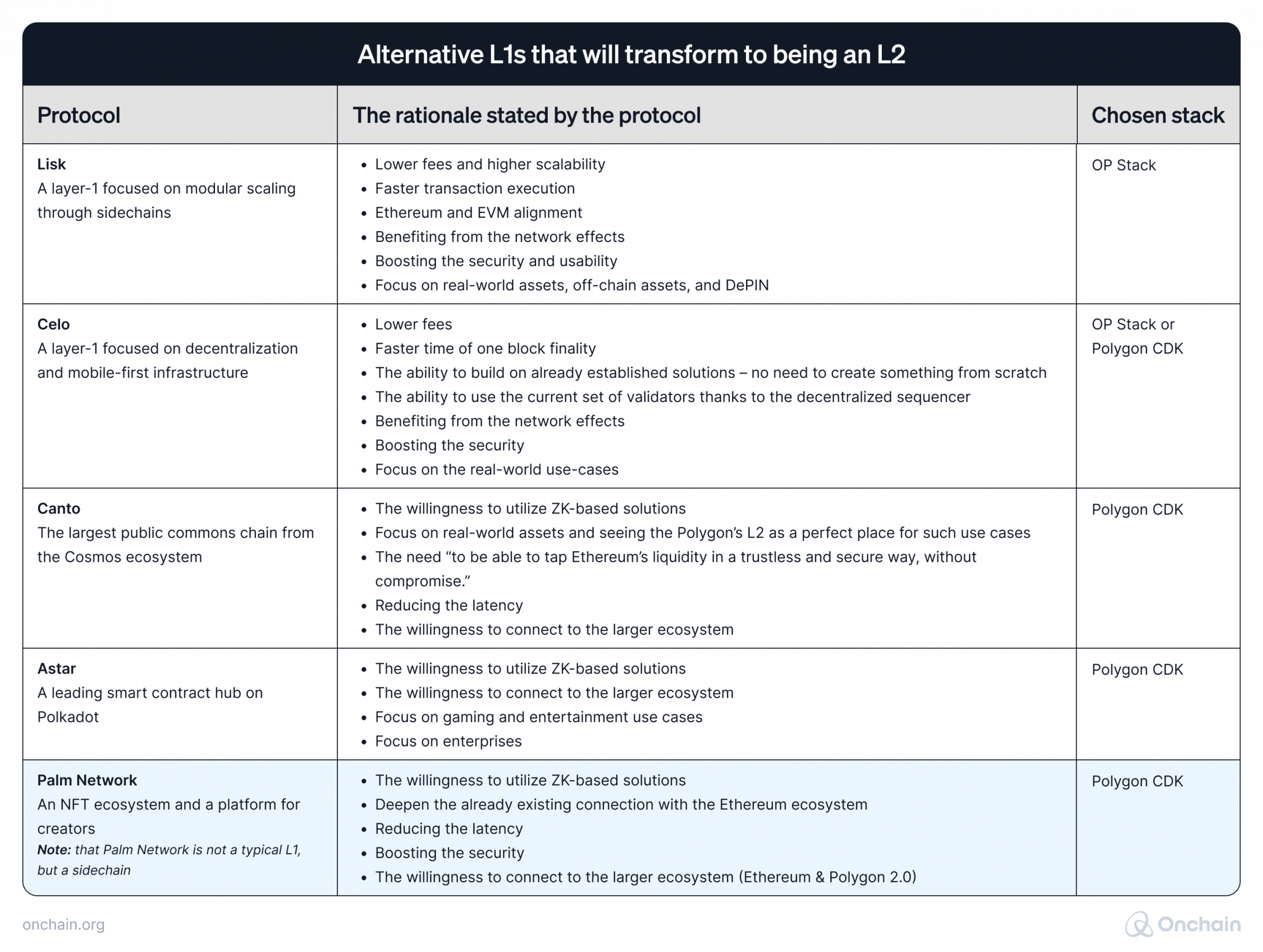
Sources: X, CoinDesk, Cryptoslate, The Block, BSC News, projects’ own media
This list is likely to grow in the future. We’ve already heard that additional protocols contemplate transitioning to a Layer 2 type, or establishing a Layer 2 blockchain as a test, if certain conditions are met.
It’s usually the safety, user experience, and self reliance that encourages L1 blockchain to transform into being an L2. – Henri Lieutaud, Head of Developer Relations at Starknet Foundation.
2. Companies establishing L2s instead of alternative L1s
The Layer 1 to Layer 2 transition is undeniably a complex and strategic decision. It’s also a lengthy process, as the case of Celo proves. During the DevConnect Istanbul conference, they explained that it was important for them to preserve their protocol features (e.g., very fast block finality), which makes the entire transformation more difficult and slows it down.
Hence, protocols and centralized companies often decide to experiment by launching a Layer 2 along their essential services. It enables them to test the solution, but preserve them from business FOMO (created if they didn’t try to capitalize on the current trends).
An interesting phenomenon is that many of these companies have launched, or plan to launch their Layer 2 despite not having a Layer 1 infrastructure before. It may indicate they always had a need for blockchain technology, but waited for an appropriate technical solution and simplification.
Below a list of companies that established Layer 2 blockchains.
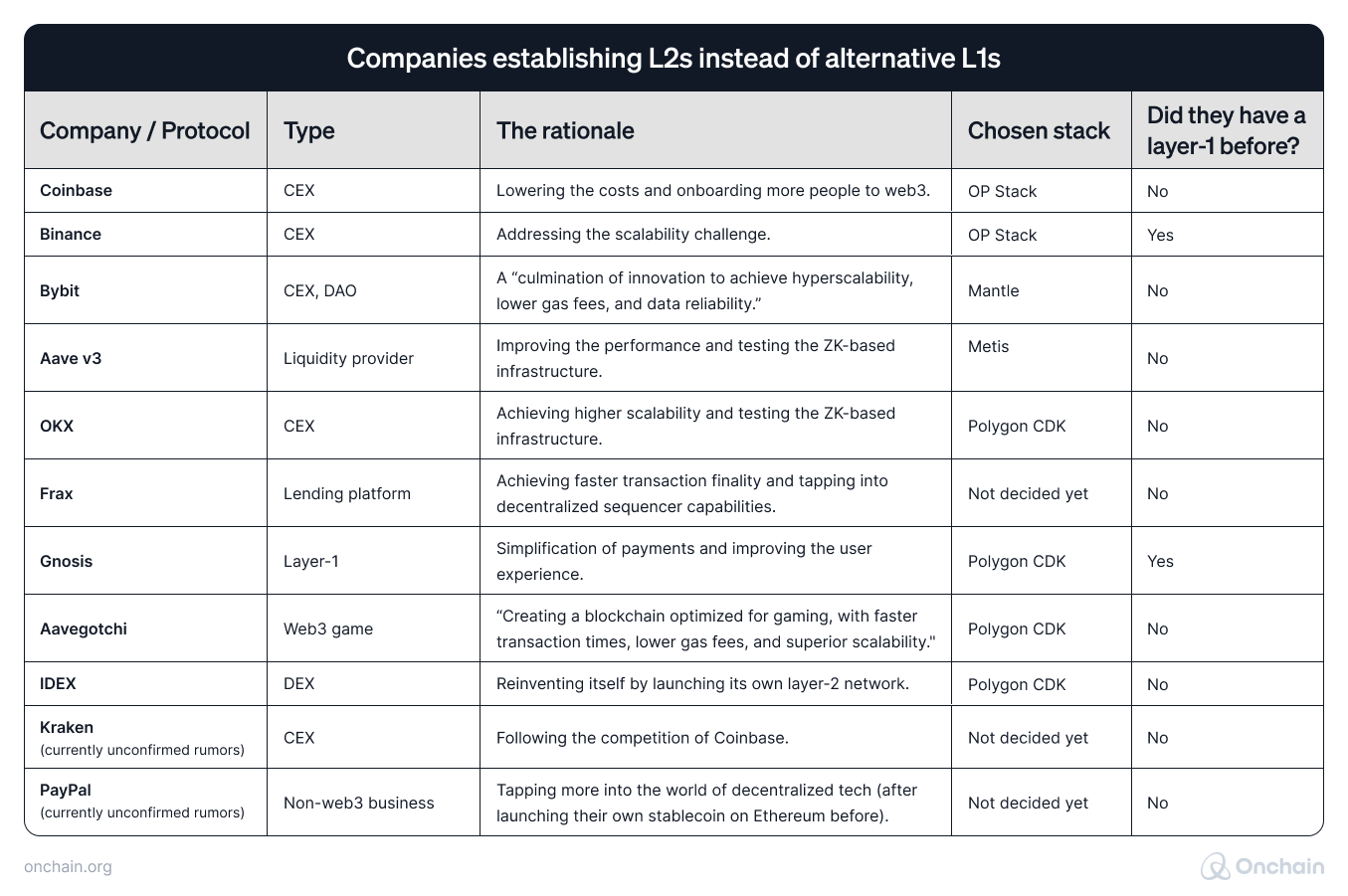
Sources: X, CoinTelegraph, CoinDesk, Blockworks, The Block, Coinbase, Bybit, projects’ own media
As always, there are some exceptions, proving the rule:
- dYdX decided to move away from Ethereum (to Cosmos) in order to build a “purely decentralized” order book exchange.
- Maker may move to Solana instead of focusing on Ethereum.
- OnChainMonkey moved its 10,000 NFTs from Ethereum to Bitcoin (as ordinals) – due to a more secure base layer and a chance to capitalize on the recent hype around ordinals.
However, the trend for companies and protocols deciding to launch a Layer 2 or transition from Layer 1 appears pretty clear. Those that don’t are likely to explore similar opportunities by:
- Launching test chains
- Monitoring the sentiment by “considering such an option”
In the future, we expect an increase in both types of activities. The reasons are that it’s getting simpler to launch a Layer 2 and it’s a chance to get publicity and (in some cases) pump the token’s price based on rumors about a Layer 2 launch or transition.
3. BUIDLing activity and use cases
We know that they move and transition. But do they BUIDL?
The number of dApps on various Layer 2 chains is growing fast. Even when we compare Layer 2s to Layer 1s with the highest market cap, we can clearly see that builders frequently use scaling solutions. Basically, if we remove the BNB Chain from the big picture, we’re left with Layer 1s that show notably lower frequency in app building activity than their Layer 2 counterparts.
Of course, many of these apps were previously built on Layer 1s and then launched also on Layer 2s, so we don’t consider all of them native to Layer 2s. Nevertheless, these numbers show the speed of adoption and development on Layer 2s.
It’s also worth looking at Base and zkSync Era, the most recently launched Layer 2s. Building activity on these chains not only outperformed the majority of alternative Layer 1s but also put them immediately on the podium in the Layer 2 category.
The following table compares various Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains and their app building activity.
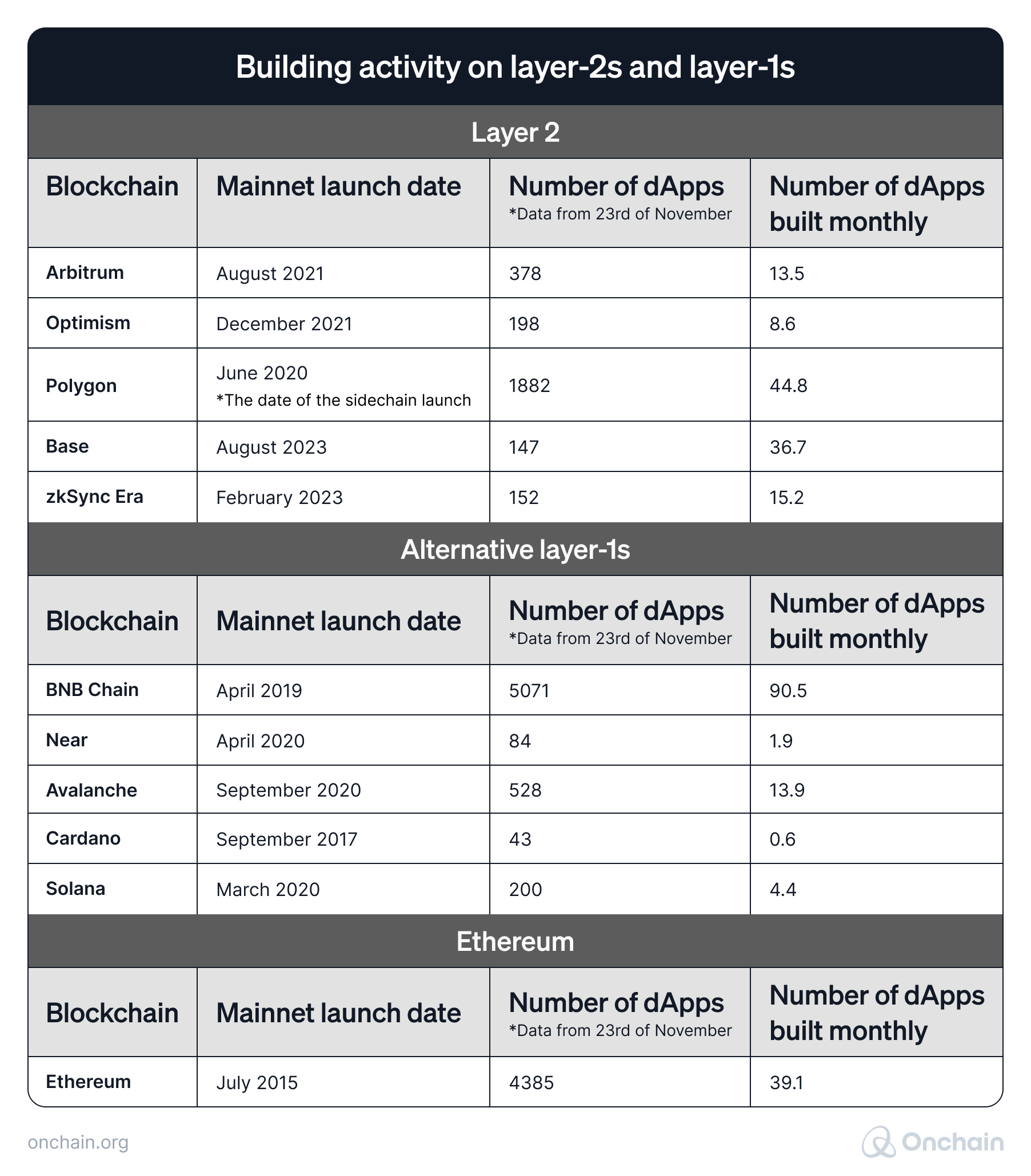
Source: DappRadar
In search for quality and value
When evaluating a blockchain, we should also look beyond the numbers and ask the question of quality and real-world impact of the dApps. On Base or zkSync, for example, the speed of BUIDLing looks very promising, but is it about creating value outside of Web3 or building yet another DEX for crypto traders?
We’ve taken a close look at the actual dApps built on chosen Layer 2s. Below, you will find the most interesting applications and, in our opinion, the most significant when it comes to real-world impact.
The most valuable projects built on L2s
The business case for Layer 2s
Now that you have an overview of the market, including trends and players, we’ll introduce financial aspects. This space is not exclusively about onchain data, but about making tangible money; an aspect that is easily forgotten by Layer 1 representatives and protagonists. But it is part of our unavoidable business reality and no one can afford to ignore it.
Let’s quickly remember the blockchain tetralemma as discussed in the first section of this report. The inability to solve the Layer 1 trilema between scalability, security and decentralization leads to inefficient operations resulting in low profitability potential. Profitability functions as an additional axis, because without profit there is no justification for any business to exist, creating a tetralemma.
Layer 2 blockchains came to break this balance by enabling better scalability. Below, we focus on how Layer 2s affect typical crypto business models and discuss the current state of VC investments in these solutions.
How Layer 2s improve blockchain businesses
Layer 2s essentially introduced a new business model to the blockchain industry by becoming resellers of blockspace. These are the steps:
-
1.
Layer 2s purchase blockspace on the Ethereum chain, which tends to become expensive in times of high congestion.
-
2.
They process transactions conducted specifically on the Layer 2. This way, they’re able to remove all computations from Ethereum and avoid paying fees for each of them.
-
3.
At the same time, a Layer 2 takes fees from each transaction conducted on its chain. Naturally, fees are significantly lower due to a more efficient infrastructure on Layer 2 than on Ethereum. This attracts developers and improves user experience.
-
4.
After processing all transactions, a Layer 2 bundles them and posts them on Ethereum. At this point, Ethereum fees have to be paid again. However, because it’s only one batch of transactions rather than hundreds of individually posted interactions, the charge is significantly lower.
By earning their own transaction fees and paying only a fraction of the amount for Ethereum’s blockspace, Layer 2s can run a blockchain more efficiently and earn an actual profit on the margin.
The DeFi Report very fittingly compares Layer 2s to credit cards: They enable us to avoid individual bank transfers whenever we want to purchase something. Instead, they try to batch transactions, improving both the throughput (we don’t have to wait hours until the transfer is settled on a particular bank account) and cost-efficiency (no additional fees incurred).
Use case investigation: Friend.tech x Base
A recent good example of generating business on a Layer 2 infrastructure is the friend.tech app launched on Base. We wanted to understand how they became profitable so quickly and what the chances of duplication were.
What is Friend.tech?
It’s a decentralized social network that enables users to “invest” in their favorite X influencers and KOLs. In exchange, they receive yield opportunities (similar to flipping NFTs) and also access to private chat rooms with their X heroes.
The impact
This idea sounded speculative, and initially, the app attracted mostly opportunistic crypto investors. However, the numbers outperformed the vast majority of Web3 apps.

The achievement
Thanks to the high popularity and low-cost infrastructure behind the app (Base Layer 2), friend.tech achieved a revenue of 10,000 ETH within only 3 months. Also, the company allocated around 50% of revenue to the project’s development team, which reported a profit of nearly $20M. Who wouldn’t say no to such money in the Web3 space?
Needless to say, friend.tech served as a catalyst for the growth of the entire Base Layer 2. It helped boost the entire protocol to record over $5M in total profit (November 2023), just 4 months after its launch.
These numbers – Base profit and friend.tech profit – clearly show how efficient dApps can become thanks to the Layer 2 infrastructure. Having said that, a speculative atmosphere around them without users’ interest, won’t make the app efficient and profitable – even on Layer 2.
According to the Daily Hodl, which closely monitored Freind.Tech’s numbers, the TVL plummeted and the new user growth rate flattened over the past two months (Oct-Nov-2023) after the initial success. These statistics teach us that Layer 2 architecture provides the technological potential for more profitability, however, whether a dApp can leverage that depends on users’ interest and other factors. That’s why L2 technology should be connected with the ecosystem that can provide the desired network effects in the long term.
How do investors feel about Layer 2s? / Investment funds are coming in waves
The final question businesses need to ask is whether the “big money” of VC funds also follows general trends. After all, without their investment, startups have little chance in any environment.
We can begin on an optimistic note. All the major Layer 2s and Ethereum scaling solutions received a significant amount of funding that encourages their further development. See the below table for amounts invested in prominent Layer 2 solutions.
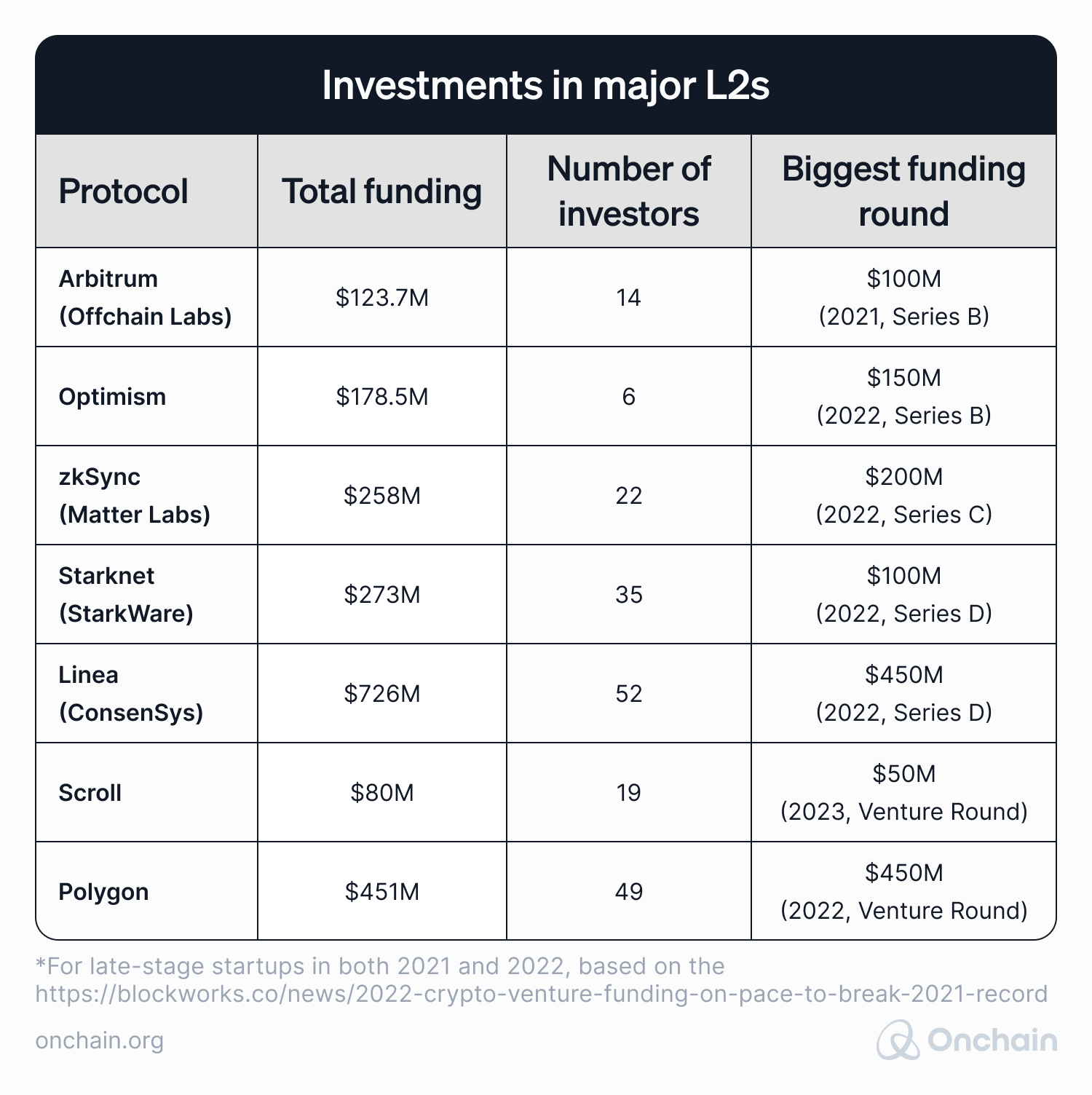
Source: Crunchbase
When looking closer at the data, you notice that the majority of the significant deals happened in 2022. On the one hand, there was a lot more ‘noise’ around Layer 2s in 2022 compared to 2021. On the other hand, Web3 funding by VC decreased massively toward the end of 2022. Layer 2s tried to maintain the interest level and stay well above the market average.
It’s interesting to point out that Linea’s and Polygon’s funding were both in the TOP3 highest crypto funding rounds in 2022, with much smaller and less-recognizable Scroll still maintaining its place in TOP10 for 2023.
When comparing VC’s interest in Layer 2s and Layer 1s, we notice that Layer 2 prevails. The below Galaxy Research graph indicates that both categories were on the decline in 2023Q3. In previous quarters Layer 2 received slightly more attention, however the highest discrepancy can be seen in the period from 2022Q4 and 2023Q2.
Share of crypto VC capital invested by category
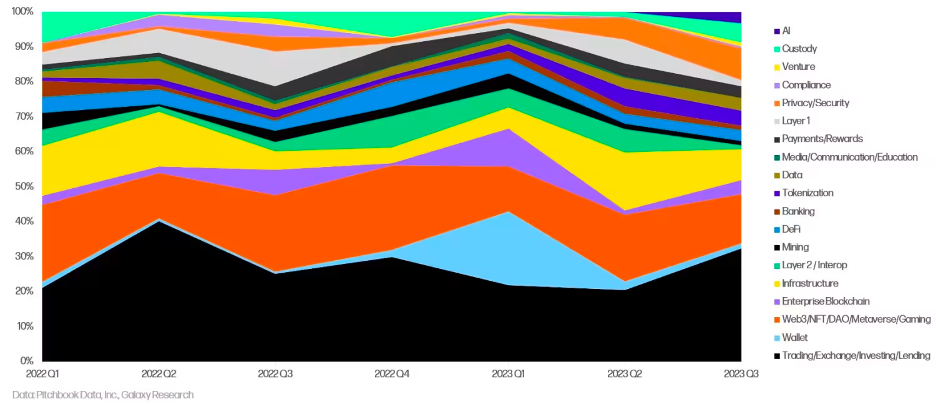
Based on combining all the finance-oriented points above – profitability, business model, users’ interest, and VCs’ involvement in early 2023 – we can presume that the Layer 2 category has a higher chance of rebounding from a poor 2023Q3 period. Venture capital firms prefer the industries where the “real money” is.
The newest Layer 2 on the market, Blast, provides another signal supporting the assumption. It launched in late November and recorded $30M of funds locked for a future airdrop. Blast is also backed by a $20M funding round led by VCs: Paradigm and Standard Crypto.
Alternative Layer 1s following suit
Do the findings regarding market moves, onchain metrics, and investments mean that no Layer 1 (except Ethereum) can make it?
We don’t have a crystal ball, and we’re far from seeing the future of Web3 in a single color. Both Ethereum and Layer 2s face their unique spectrum of challenges. At this point it’s too early to expect them to address all the challenges and concerns of using and building on blockchains. The development of the Web3 landscape is an ongoing process and there’s room for diversity.
We want to showcase a few projects that, due to their unique characteristics, are worth mentioning and might become a valuable alternative to the Ethereum & Layer 2 tandem. This doesn’t mean other projects are doomed to fail. However, in our opinion, a protocol needs to offer more than faster and cheaper transactions, to become a preferred solution for entrepreneurs and users in the already cluttered Web3 industry.
Cosmos
Cosmos can compete with Ethereum when it comes to earning the term “internet of blockchains.” Ethereum earns it thanks to its general dominance and emergence of Layer 2s with other blockchains built on top of them. Cosmos continuously strives to build an ecosystem of independent app-specific chains called zones connected with each other via interoperability. Cosmos allows for more independence of the blockchains within its ecosystem, because they don’t have to rely on the Layer 1 as much as Ethereum-based rollups and dApps.
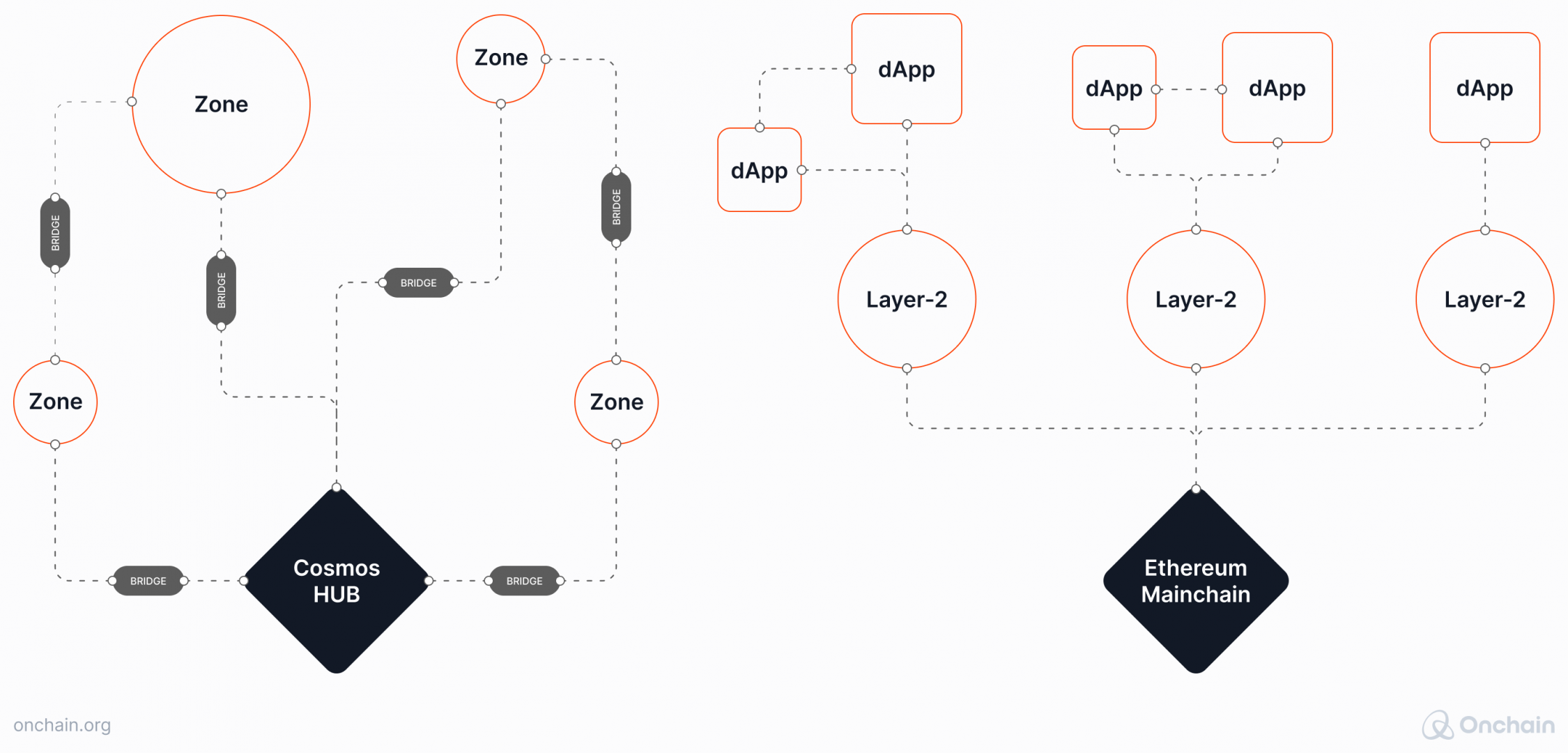
In practice, the solution initially worked well. Thanks to its unique architecture as well as accessible and easy-to-use SDK, Cosmos attracted well-known projects, such as:
- Binance Smart Chain (now BNB chain) – the official Layer 1 for Binance.
- Cronos – an EVM chain maintained by the Crypto.com exchange (secured by its CRO cryptocurrency).
- Terra – now the infamous protocol aimed at building an ecosystem of purely decentralized stablecoins.
- THORSwap – currently one of the TOP5 DEXs in Web3, with a built-in cross-chain interoperability.
As time passes, challenges arise for Cosmos and 2023 has been a difficult year. The implementation of its (r)evolutionary Atom 2.0 update keeps getting postponed, giving the competition time to catch up. The protocol’s main features – interoperability, shared security, and efficiency – are no longer unique mostly due to the emergence of Layer 2s that serve a similar purpose when combined with Ethereum.
Still, a developer or user looking for an established and accessible ecosystem outside Ethereum, might find Cosmos to be the best solution. Its SDK remains the market benchmark. The existing apps in combination with a strong community smoothen the onboarding process and enhance the overall blockchain experience. And let’s not forget, that Cosmos offers more independence and is the optimal option for those who prioritize freedom. The only “more sovereign” alternative would be to basically launch another Layer 1.
Hence, we see Cosmos as a potential complementary solution to Ethereum, serving very specific, independence-oriented use cases.
Celestia
Celestia is the most popular example of a modular blockchain paradigm. It breaks down a typical blockchain into several specialized layers and enables each to focus on one function only:
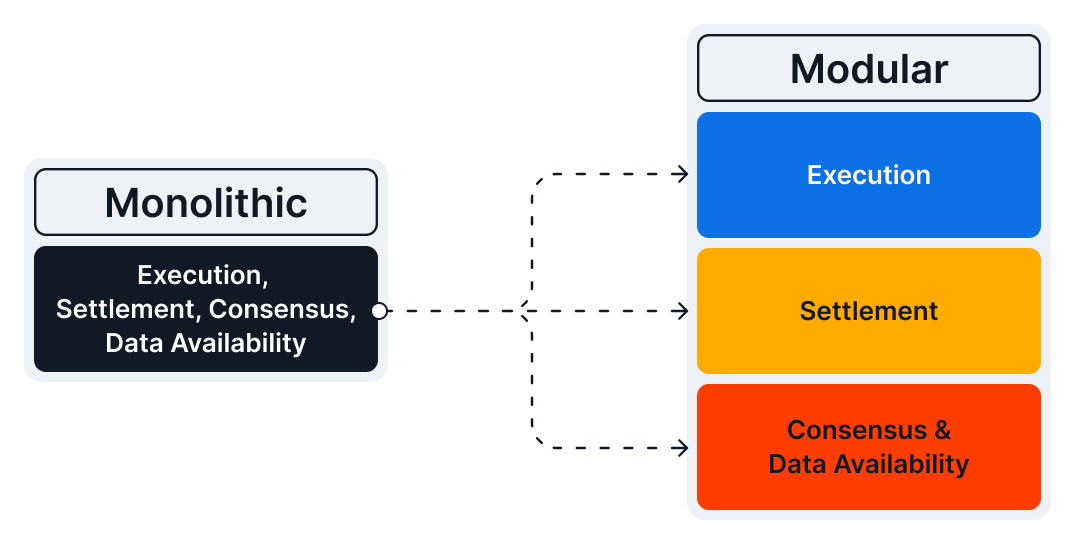
Source: Celestia - A comparison between monolithic and modular blockchains
Celestia takes care of the data availability and consensus. At the same time, it enables other protocols to build on top of it (providing execution and settlement, and consensus layers), aiming to create an ecosystem of interconnected, specialized chains.
It’s a bold idea that, in theory, addresses some of the struggles of monolithic blockchains like Ethereum. This is elevated by the fact that Celestia enables various rollups to join its ecosystem and maintain higher sovereignty than they would, were they connected to Ethereum.
It’s too early to predict the future of modular blockchains. Celestia was launched in October 2023. However, we can already see some interesting examples of how completely different and seemingly competing chains may work together based on a non-monolithic approach. It’s definitely a project to keep an eye on.
TON Network
Contrary to the two projects we described before, TON Network doesn’t seem to have a revolutionary technical infrastructure.
However, it has a potentially much more important advantage in the long term. TON became the underlying blockchain for Telegram, granting it access to a nearly unlimited number of potential users.Since September 13th, 2023 Telegram users are able to create their own non-custodial wallets and use the TON network. We’re talking about a group of 800 million active people, a number that immediately surpassed the number of other established Layer 1s such as Solana, Cardano, and Algorand combined.
It remains to be seen whether TON will be able to capitalize on its early advantage and its unique opportunity. All the other chains would prefer the inflow of such high user numbers over a longer period rather than within one day. Taking into account the backing from Telegram as well as the already promising infrastructure (TON holds a record for blockchain network speed), TON may emerge as a sincere contender to Ethereum in specific use cases, such as quick in-app payments and decentralized social network infrastructure.
Does Ethereum’s dominance signal Web3 market maturity?
Zooming out and looking at the bigger picture of general business and management theories, some of the points above suggest that the blockchain space is actually maturing. We have Ethereum + Layer 2s as one dominating ecosystem, a small group of ambitious competitors, some niche companies, and the declining performance of many projects that emerged in the early market.
The Law of Duality
These points lead us to the Law of Duality, one of the famous Immutable Laws of Marketing coined by Jack Trout and Al Ries.
- In their opinion, “in the long run, every market becomes a two-horse race.” It can be seen in examples such as Android vs. iOS mobile operating systems, Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi in the FMCG industry, or Microsoft vs. Apple in the general IT space.
- If we had to pick a “horse” in the Web3 market race, we would definitely bet on Ethereum – based on the data and arguments provided in this report. Accompanied by Layer 2s, it is likely to advance into an even more dominating force in the industry, powering the majority of dApps and attracting the highest number of developers.
- Identifying the second “horse” to fulfill the duality is a completely different story. Would it be Solana (despite its problems) along with its enthusiastic community? Will Cosmos and its exceptional approach to creating a Web3 ecosystem fill the spot? Or might modular Celestia connecting Layer 1s and Layer 2s into a new type of infrastructure end up grabbing the title? No matter our prediction, they are still only speculations and it’s clear that it’s too early to call the space mature and claim it’s already following this general market theory.
Industry Life Cycle
The second prominent business model, the Industry Life Cycle, also suggests that it’s not time to describe the blockchain space as mature yet. When we look at the chart and criteria below, it’s possible to place the industry somewhere between the “Growth” and “Shake out” phases. And judging by the current speed of BUIDLing and innovation, the market will benefit from prolonging the current state.
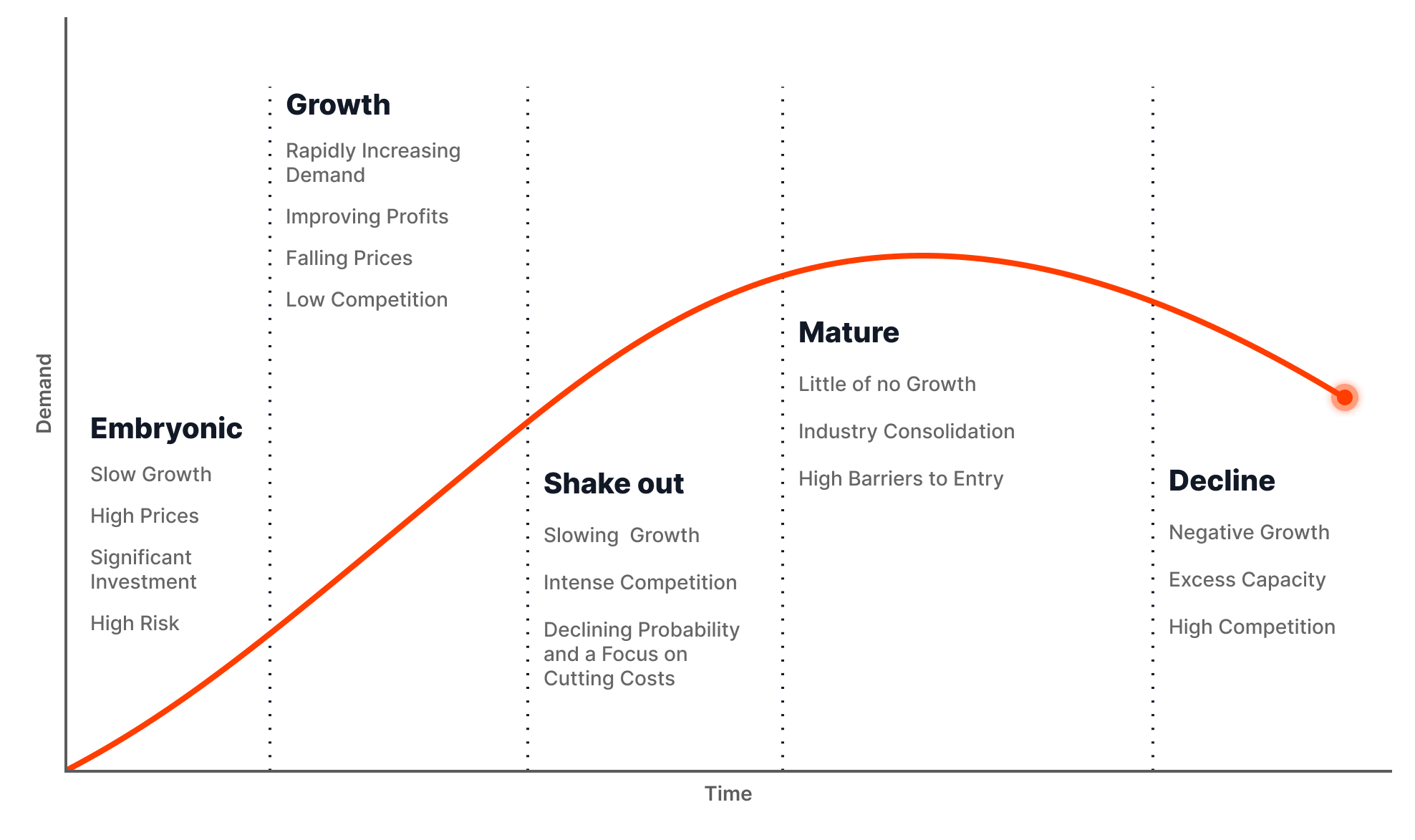
Source: AnalystPrep
It follows that we might learn more from focusing on the “hype cycle” instead of the “life cycle”, when analyzing the current state of the blockchain industry from the business theory perspective. Gartner, one of the leading research entities in the world, created a methodology of looking at emerging innovations, concepts or brands that can help us assess the current status and future expectations around Layer 1s and Layer 2s.
Based on Gartner’s basic hype cycle idea, we created our own hype cycle for Ethereum, alternative Layer 1s, and Layer 2s, by placing them in the appropriate stage on the curve. The placement is based on the findings presented in this report and serves as a visual summary. It is also a projection forward and, therefore, a kind of forecast.
The goal is to highlight projects that are the closest to breaking away from the hype around blockchain and growing into a mature solution for both entrepreneurs and enterprises.
We based our decision where to put specific protocols on the following criteria:
- General sentiment around projects
- General hype around projects
- General state of development of projects
- Recent VC investments in projects
- Recent events around projects
- Onchain data for projects
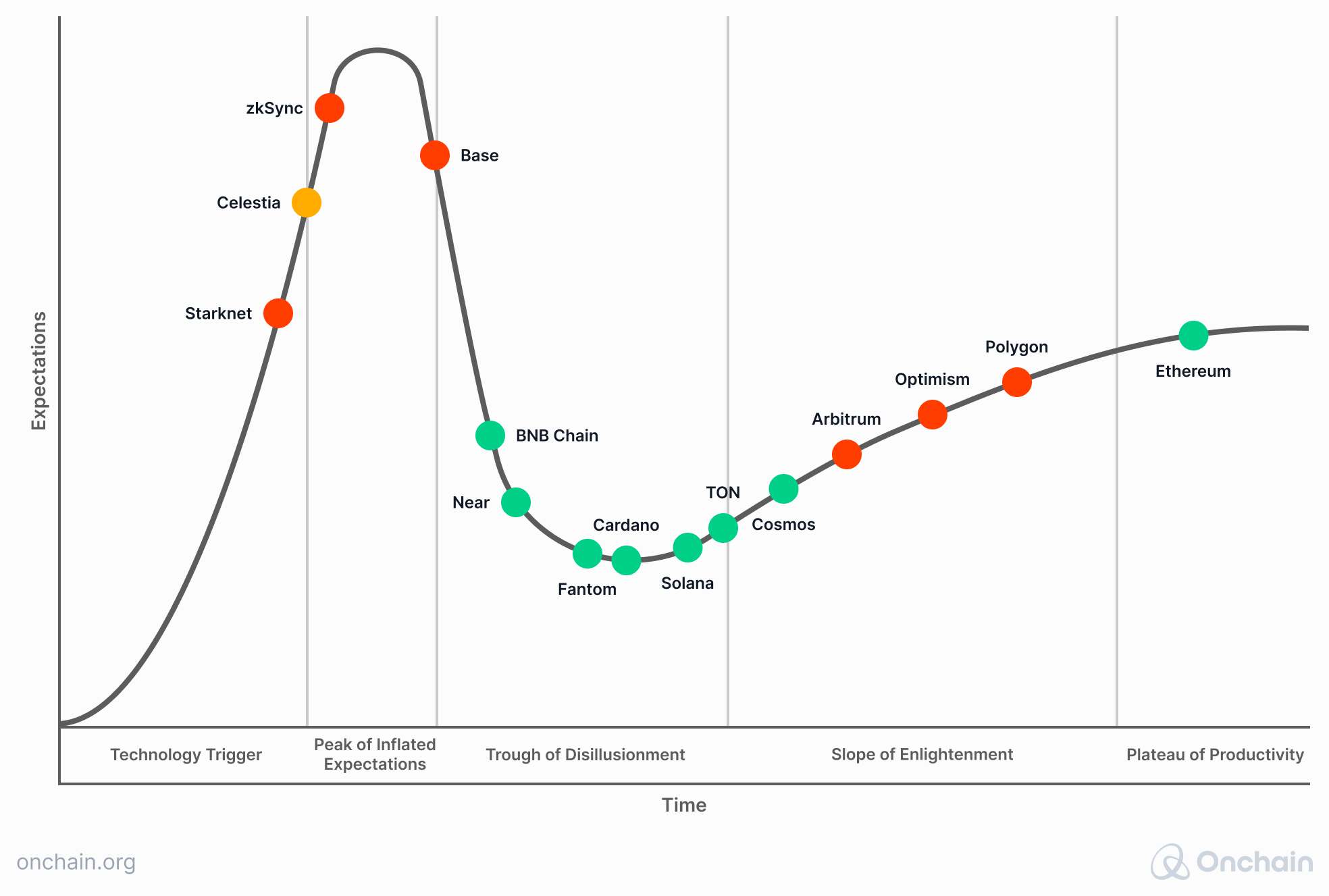
The graph clearly demonstrates that following Ethereum, the established Layer 2s have the best chance of maturing in the short term. Polygon still attracts VCs and has a growing adoption rate among enterprises. Optimism and Arbitrum maintained the development growth.
At the same time, most Layer 1s currently appear in the phase where they need to explore options to transform to stay relevant. Based on the multiple factors explained in the previous sections, they can either find a new path (as, for example, Lisk or Canto did) or remain in competition for users and developers with Ethereum & Layer 2s. However, considering this tandem’s dominant position and the need for the blockchain market to mature, the majority of alternative Layer 1s will struggle to break away from the hype cycle and forge ahead to become the preferred solution for entrepreneurs and individuals.
Conclusion
- To say that the Web3 industry before the introduction of alternative Layer 1s was limited is to say nothing at all. Both non-programmable Bitcoin and non-scalable Ethereum provided essential value for developers, investors, and entrepreneurs willing to build on blockchain. But they were definitely not enough to ignite a much needed dApp revolution.
- Emerging alternative Layer 1s provided a breath of fresh air just when progress seemed to suffocate. Their speed, scalability, and technical innovations caught a lot of attention, leading to a drastic increase in the number of solutions created. Fast forward another few years, though, and the space is gasping for air again. It turns out, the proposition of alternative Layer 1s is not good enough to enable the mass adoption of blockchain.
- After nearly 9 years on the market, Ethereum remains dominant, and the introduction of Layer 2 scaling solutions further strengthens its position. This combination addresses both blockchain trilemma and network effect struggles encountered by other Layer 1 blockchains. In addition, it supports Web3 business by enabling network participants, app builders, and entities behind protocols, to establish non-speculative revenue streams.
- Any forecast should always be taken with a grain of salt. No one can predict with certainty how technology and markets will evolve, especially when they are still far from being mature, like blockchain infrastructure is. However, some cornerstones have been laid, and whatever comes next must take them into account. For blockchain development it means, taking Ethereum into account. You can either build around or on that cornerstone.
- Remember the ancient saying: if you can’t beat them, join them. Despite a few promising (Solana) or already established and growing protocols (Cosmos) that try to work around Ethereum, the more promising growth potential for the blockchain industry, in our view, is on or with Ethereum. The findings of this report lead us to believe that Ethereum + Layer 2s are the future for the blockchain industry.
- We are ready and excited to spend the next years researching, analyzing, and evaluating whether our predictions were accurate.
Methodology
How did we approach the research?
The research was based on the "deductive approach" and aimed at proving or refuting the hypothesis: "Layer 2s serve as a better choice for entrepreneurs compared to alternative L1s."
Research limitations
-
This report is focused on comparing alternative Layer 1s and Ethereum accompanied by Layer 2s. Our goal wasn’t to evaluate Layer 1s or Layer 2s individually and favor one over another.
-
The set of chosen Layer 1s or Layer 2s for our analysis is primarily based on their market capitalization or factors relevant to the context of a specific report section. We were not aiming to make 100% consistent choices in this area, although we tried to refer mostly to the same projects.
-
We’re aware of the recent hype around a few alternative Layer 1s, with Solana as the most prominent example. However, our goal was not to analyze short-term trends, but to provide a more holistic and long-lasting view of the market.
-
We didn’t include Bitcoin as one of the analyzed Layer 1s because the intention is to cover only programmable blockchains.
-
Note that data, trends, and market conditions are ever-changing.
Led by
Conducted by



Contributors


