Updated on: Feb 10th, 2025. Original title: Where to Build dApps — Layer-1 or Layer-2?
As we move into the second half of this decade, the competition between modular and monolithic blockchains is heating up. The focus is shifting toward prioritizing consumers by offering faster, cheaper dApps with hidden complexity.
Innovations such as data availability layers and sovereign rollups are driving this trend, which could result in greater blockchain adoption.
Although both architectures have gained traction over the last couple of years, it remains uncertain which will ultimately outperform the other in the long run.
Therefore, we decided to give you an update here and take a look at the resurgence of modular blockchain design and its advantages.
Modular vs monolithic blockchains
Entering the ever-changing world of building dApps, understanding where both layer-1 and layer-2 protocols fit is crucial.
You should think of these as distinct architectural layers contributing to the functionality and scalability of decentralized systems. In essence, they are vital components in the blockchain architecture.
Choosing a blockchain architecture is a pivotal decision that requires careful consideration.
On the one hand, we have monolithic blockchains like Sui and Solana, that everyone is familiar with, and on the other hand, modular blockchain crypto projects such as Celestia, Cosmos, and Ethereum.
Modular blockchains have rapidly been gaining traction and are emerging as a secure, scalable, and decentralized alternative to the traditional monolithic architecture. Let’s take a closer look at what they are and how they work.
What is modular blockchain?
A modular blockchain divides the core functions into distinct layers offering clear benefits, providing flexibility and vertical scaling.
It breaks each layer down separately, enabling efficient handling of specific tasks such as execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability.
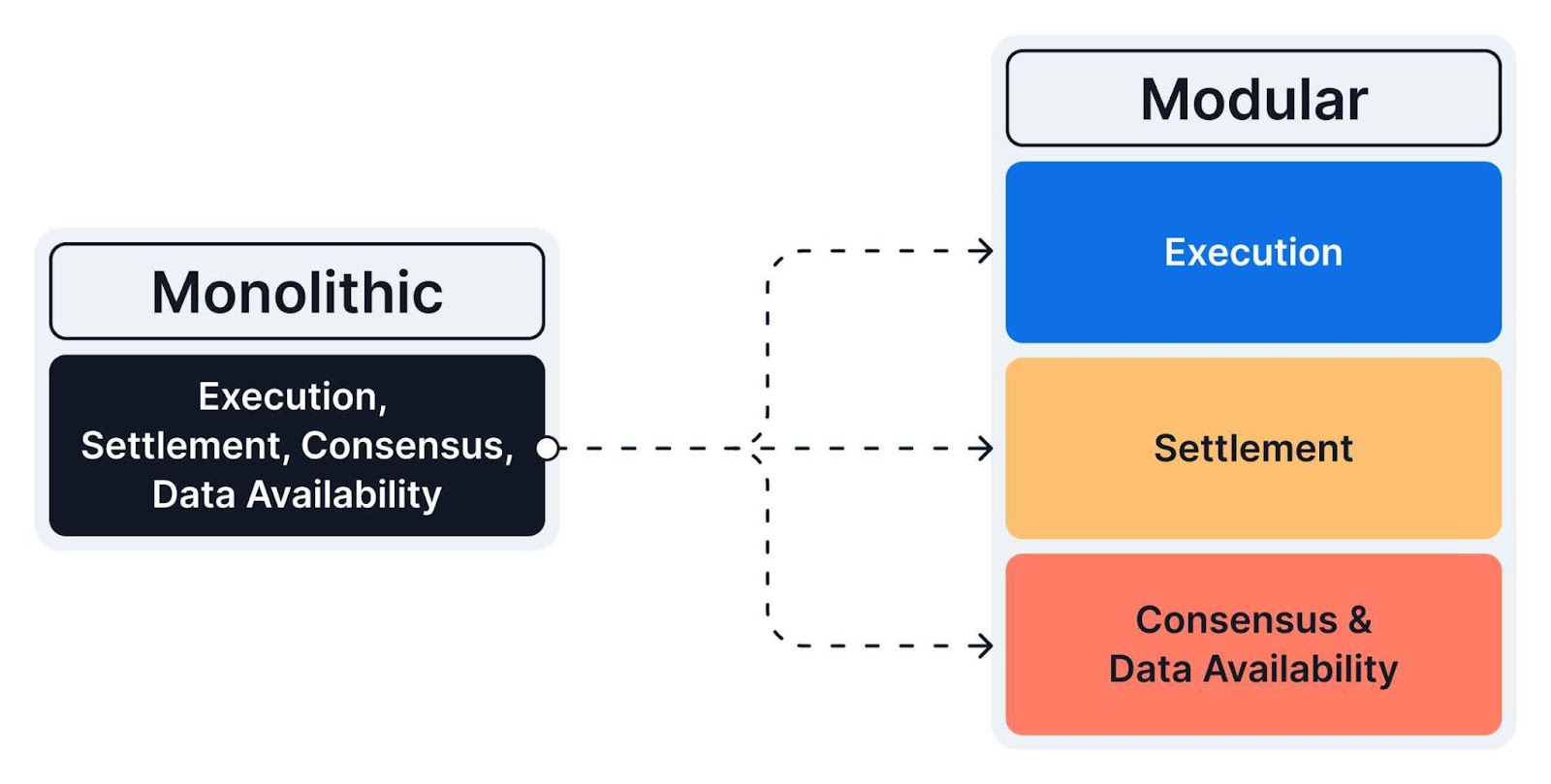
Transactions are executed to process data, settlement ensures the security of transaction destinations, consensus validates transactions, and finally, data availability manages how transaction data is stored.
Hence, modular design has significant advantages and offers a flexible, efficient approach that could resolve the blockchain scalability trilemma.
Onchain’s research report “The Future Is Modular” covers this in more depth.
A key advantage of building a modular blockchain project is that because these functions are handled in separate protocols, they can be optimized to perform their tasks independently.
Modular blockchains break down the core functions, such as transaction processing, security, and data storage, into separate layers. This enhances flexibility and scalability, so developers can fine-tune specific components without overhauling entire systems.
Solutions like Celestia and Avail offer dedicated data availability layers, helping rollups offload storage and computation.
However, this approach comes with trade-offs, as it fragments liquidity across multiple rollups, complicates asset transfers, and requires cross-chain bridges, which are costly and vulnerable to exploits.
UX (User Experience) complexity also increases as users must navigate different chains, wallets, and bridges—unlike monolithic blockchains like Solana, where everything is integrated.
Despite these challenges, modular chains improve scalability and security. To reach their full potential, they need better liquidity solutions, seamless bridging, and user-friendly experiences.
Until then, the question remains: Does modularity solve more problems than it creates?
Modular blockchain key innovations
- Interoperability:
Protocols such as IBC enhance connectivity across ecosystems, driving modular adoption. Solutions like Celestia and Avail, which are chain-agnostic, allow businesses to develop dApps or rollups compatible with multiple ecosystems. - Expanding ecosystems:
With an increasing number of modular blockchain projects and modular blockchain crypto projects being developed, scalable, low-cost, and trust-minimized environments powered by rollups and innovative solutions are being created. - Economic impacts:
Though modular blockchains have higher initial costs, they allow better value capture and customization for apps prioritizing tailored infrastructure. - Customization and scalability:
Developers can optimize execution environments for specific use cases. This results in accelerating innovation and enabling specialized solutions. - Future outlook:
Modular designs, led by Ethereum’s advancements in rollups and sharding, could enable throughputs of millions of transactions per second by 2030. High-performance chains such as Solana are also integrating rollup-like innovations.
What are Layer-1 and Layer-2 in blockchain networks?
We will cover these options in the following sections. Fully understanding them will help you navigate the right direction for your future endeavors.
Layer-1 is the base protocol. It acts as the infrastructure, enabling other applications and protocols to build on top of it. Therefore, layer-1 is often referred to as the foundational blockchain network. Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana are layer-1 networks.
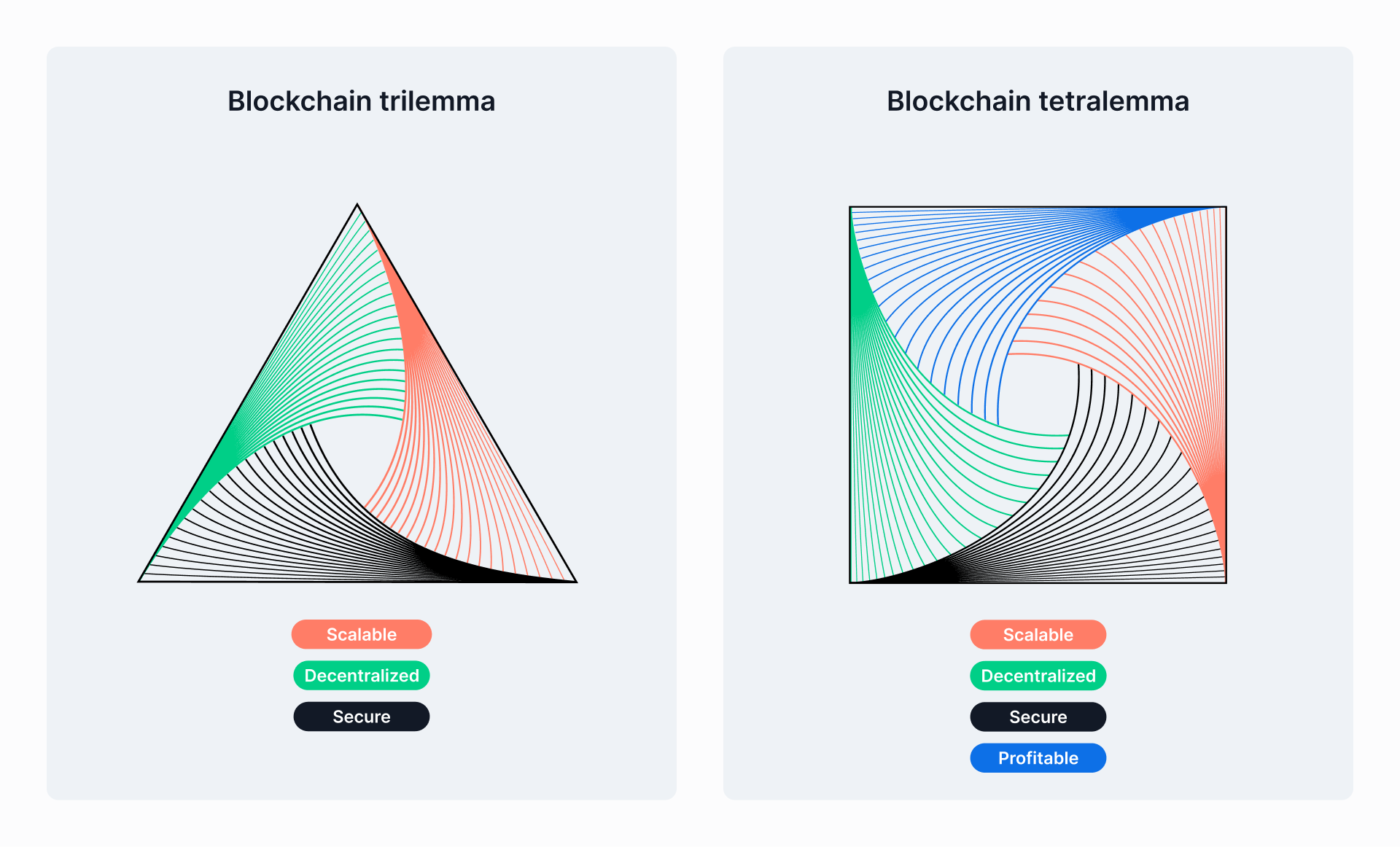
The consensus mechanism deployed within layer-1 networks involves trade-offs between security, decentralization, and speed. These trade-offs are known as the blockchain trilemma, which is explained below.
The field of consensus mechanisms is constantly evolving. For example, some networks prioritize decentralization and security at layer-1, and then they outsource speed-related functions to layer-2 solutions.
You can think of layer-2 as a supplementary layer built on top of layer-1.
In essence, it is an off-chain network residing on a layer-1 network. Layer-2 networks enhance the efficiency of their underlying corresponding layer-1 infrastructure.
This layer-2 extension augments the performance of the layer-1 network, lowering transaction fees and enhancing programmability.
Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, and Starknet are some of the layer-2 scaling solutions out there.
What is the difference between layer-1 and layer-2 in blockchain?
Certain strategies are used to address scalability and transaction processing challenges.
For example, layer-2 networks possess the ability to boost throughput. However, this can come at a cost, as it may impose a burden on the mainchain.
It could result in a compromise of security and decentralization in favor of increased throughput.
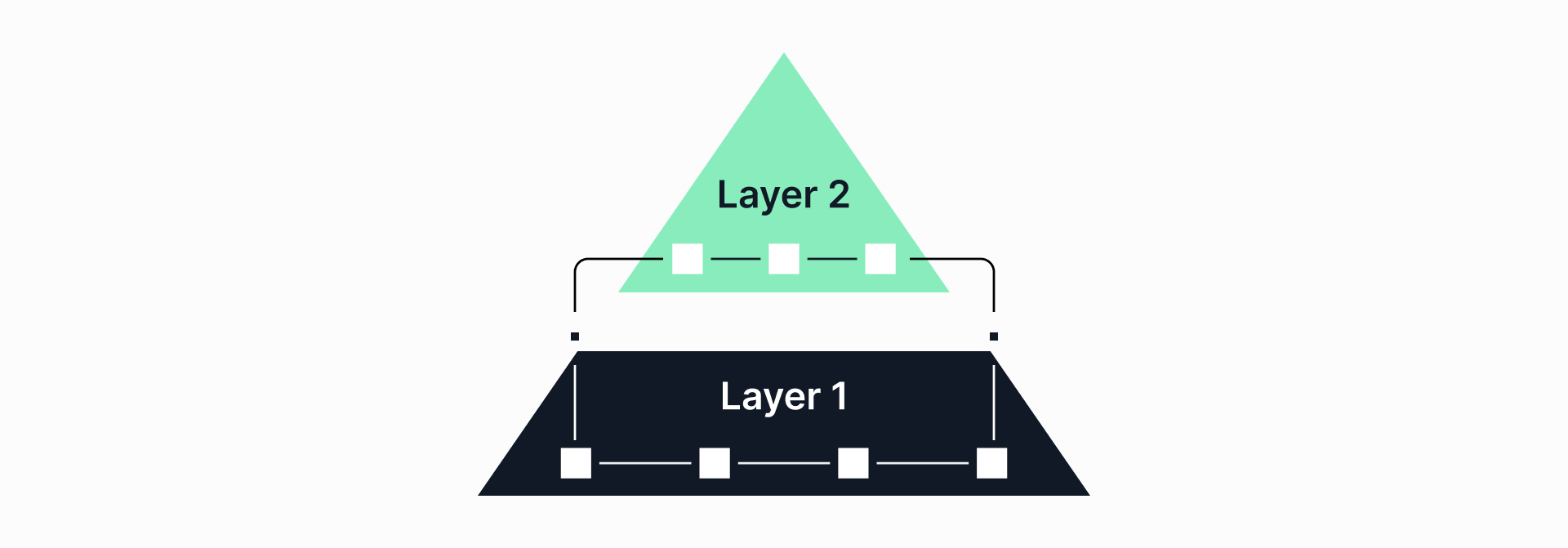
Layer-1 solutions
- Layer-1 blockchains serve as the foundational infrastructure for decentralized applications. While some L1s, like Ethereum, face high transaction costs, others, such as Solana, Sui, and Avalanche, are optimized for cheaper transactions and faster execution.
However, this scaling comes with trade-offs. These networks often rely on fewer validators or alternative consensus mechanisms, prioritizing speed over decentralization and security.
Layer-2 solutions
- Layer-2 solutions help scale networks that struggle with fees and congestion, but cost alone is not the only factor. Developers want to build where the most users and liquidity are present.
Strong network effects matter, and Ethereum’s layer-1 remains dominant because of its deep liquidity, established ecosystem, and seamless composability between dApps.
Looking at both solutions, newer L1s and modular solutions face challenges with fragmented liquidity and a more complex user experience, which makes cross-chain interactions more challenging for users.
Using layer-2 allows for authenticated off-chain transactions, which offers new features without compromising existing structures.
Modular blockchains and alternative L1s bring innovation, but their success will depend on improving liquidity accessibility, reducing UX friction, and ensuring better interoperability.
The limitations of layer-1 solutions led to research on scalability in layer-2 protocol, such as by the Ethereum Foundation and various other entities. But what about layer-3?
Bringing layer-3 into the mix
The primary merit of a layer-3 scaling solution is its ability to enhance scalability. It does not require alterations to the existing blockchain infrastructures.
Each transaction requires on-chain settlement as fast as possible.
Reducing settlement times can provide a financial incentive, enabling faster trading and other financial operations and increasing profitability. This means the blockchain system must not compromise on the on-chain settlement time (OCST).
If we now introduce the OCST property, this leads us to a Tetralemma. In the Tetralemma framework, a system is capable of embodying 3 out of the 4 specified properties.
Why do layer-2s matter, and why do we need layer-2 solutions?
Layer-2 protocols aim to enhance the blockchain’s scalability and effectiveness. As the decentralized Web3 landscape expands, it encounters scalability issues.
Layer-2 solutions tackle these by providing faster transactions, optimal performance, and reduced costs, which are crucial for both your decentralized applications (dApps) and the Web3 ecosystem.
Another area to consider regarding layer-2 solutions is Ethereum’s dominance in this space. Ethereum has successfully capitalized on the layer-2 blockchain sphere.
Ethereum’s layer-2 tokens are built on a layer-1 scaling solution that addresses scalability challenges. Transactions happen faster and cheaper compared to those directly on the Ethereum mainnet.
This move towards layer-2 solutions in the crypto industry will further fortify its success. As Ethereum is one of the most popular dApp development platforms, various Ethereum layer-2 rollup solutions have emerged. These include Optimism, Arbitrum, Polygon zkVM, and zkSync Era.
As layer-2 solutions continue to evolve, they are also paving the way for more innovative projects, including those integrating AI into Web3. To delve a bit deeper, take a closer look at some of these top Web3 AI projects.
Finally, in addition to layer-2 solutions, decentralized cloud computing is playing a crucial role in enhancing scalability and performance for blockchain-based applications.
By distributing data and processing power across decentralized networks, it complements the layer-2 solutions, ensuring that dApps can scale securely while maintaining privacy and reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure.
Building dApps on layer-2
The reason why building on layer-2 is advantageous comes down to scalability. To achieve this goal, using a layer-1 solution would require higher hardware requirements.
However, this may compromise decentralization, require significant changes to the layer-1 protocol architecture, and make the project time-consuming and cumbersome.
On the other hand, to address these pain points, many developers choose layer-2 solutions. This results in a more flexible and faster alternative solution for their dApps.
To achieve this, we need to look at the key layer-2 rollups that currently exist for layer-2 scaling solutions.
ZK Rollups
Firstly, ZK rollups are an alternative solution. These also reduce transaction costs and increase scalability.
Similarly, multiple transactions are consolidated and batched together. And this results in a rollup that can then be executed off of the mainchain.
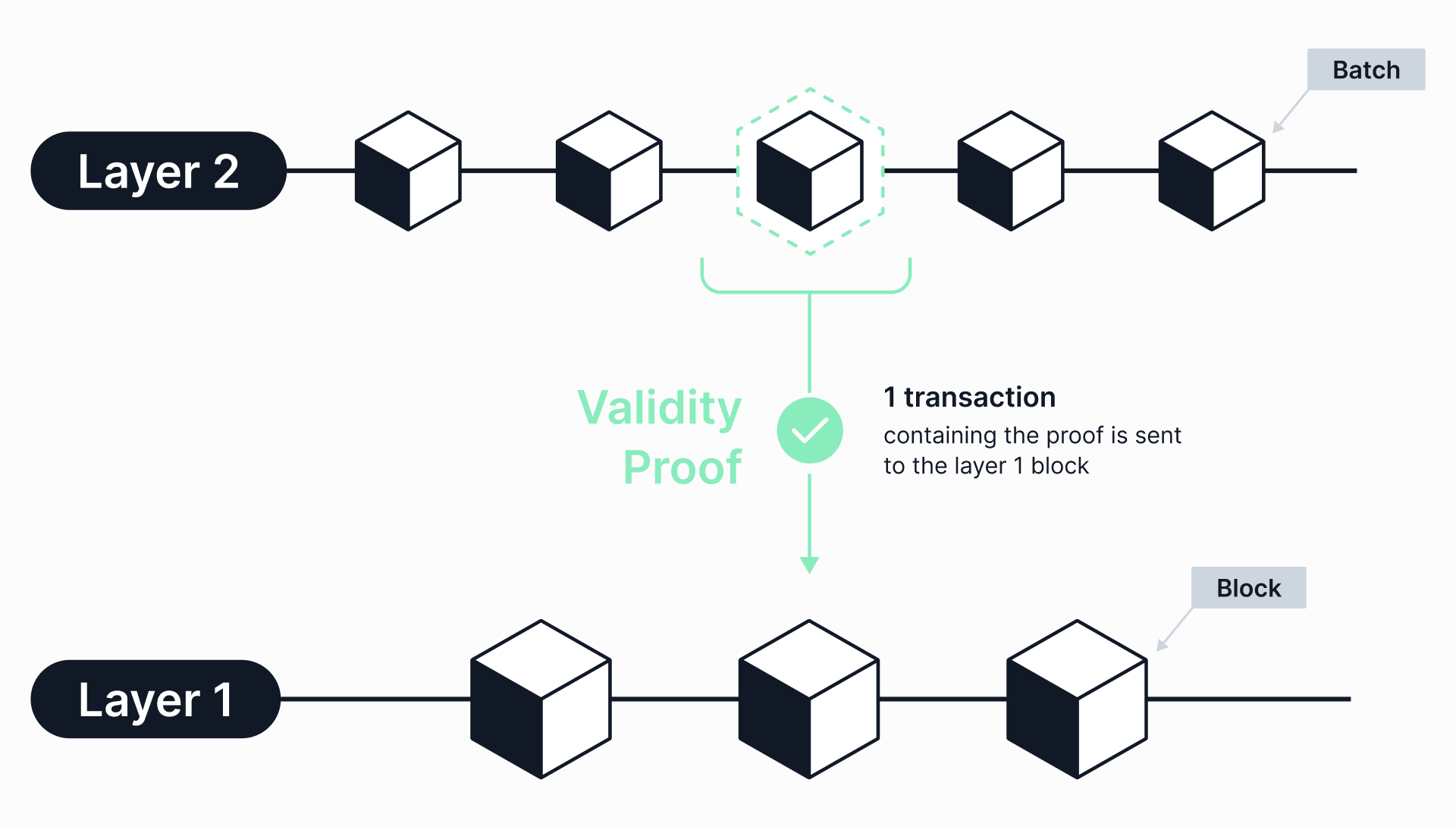
After completion, a concise summary of the changes made is submitted by a ZK rollup operator. This produces validity proofs that ensure the accuracy of the changes.
These zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are much smaller than the original transaction data. Hence, it is easier, faster, and cheaper to verify them.
These proofs are cryptographic protocols that allow off-chain transactions while maintaining validity. And they also safeguard the transaction data’s privacy and security.
Optimistic Rollups
Secondly, an optimistic rollup accumulates transactions on its chain and bundles them into a batch (rollup). It then submits them for execution on the mainchain.
The term “optimistic” is used because these transactions are considered to be valid unless proven otherwise within a specified time period.
This reduces the amount of computations, and results in lower gas fees. Furthermore, a “fraud-proof” mechanism is deployed.
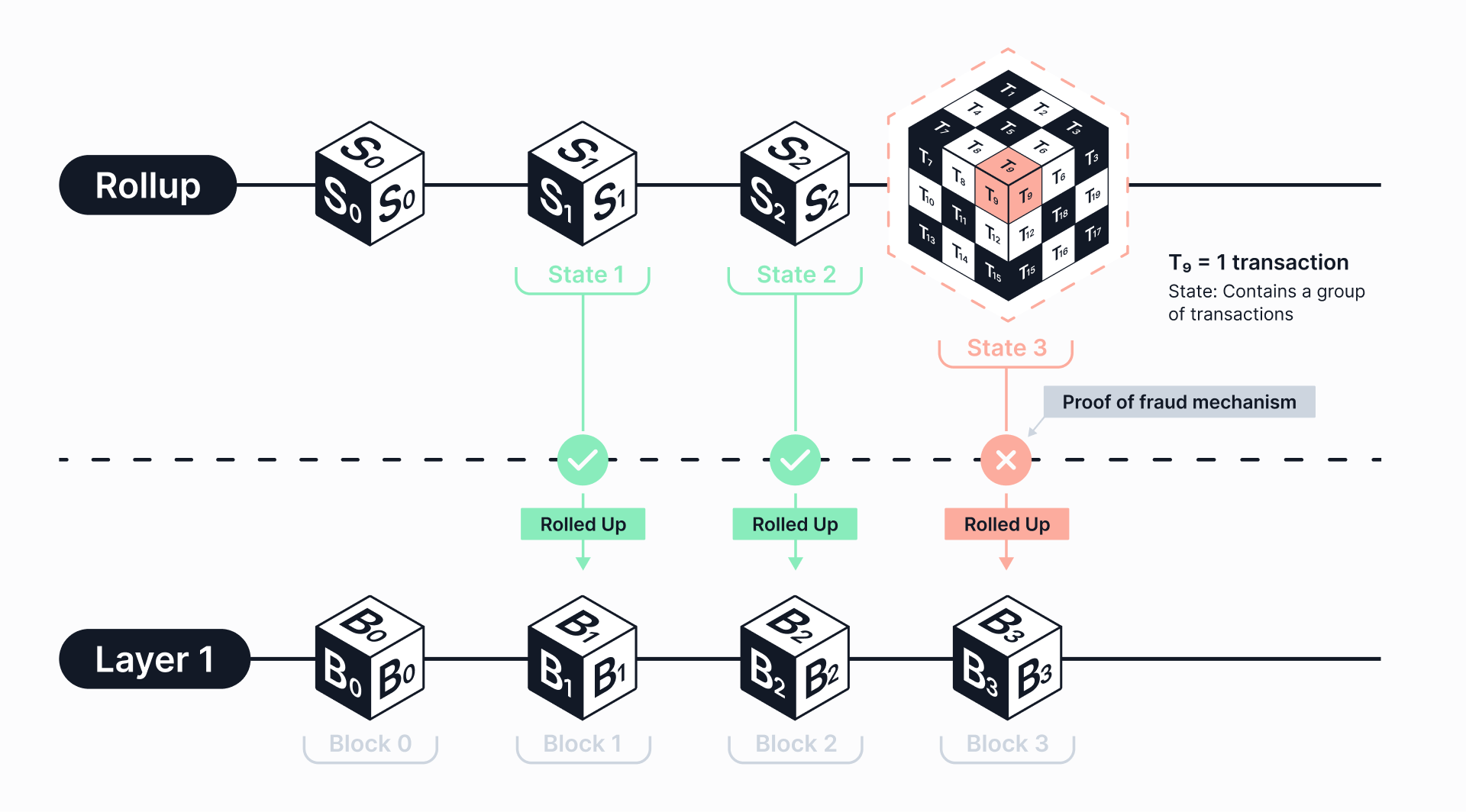
If misbehavior occurs by the block producers, then the transaction data must be accessible on the layer-1 mainchain. Compared to zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups, this solution offers native support for smart contracts. Therefore, developers are easily able to deploy their dApps with only minor code adjustments on the layer-2 network.
Rollups-as-a-service (RaaS)
Finally, rollups-as-a-service, (RaaS) products are designed to offer a simplified, elastic, flexible, pay-as-you-go model. It can consist of different rollups, which would be a custom-built solution. These will reduce the complexity and time to complete your project.
There are various RaaS providers out there where you can outsource this entire process.
An overview comparison between optimistic rollups and ZK rollups can be seen in the table below:
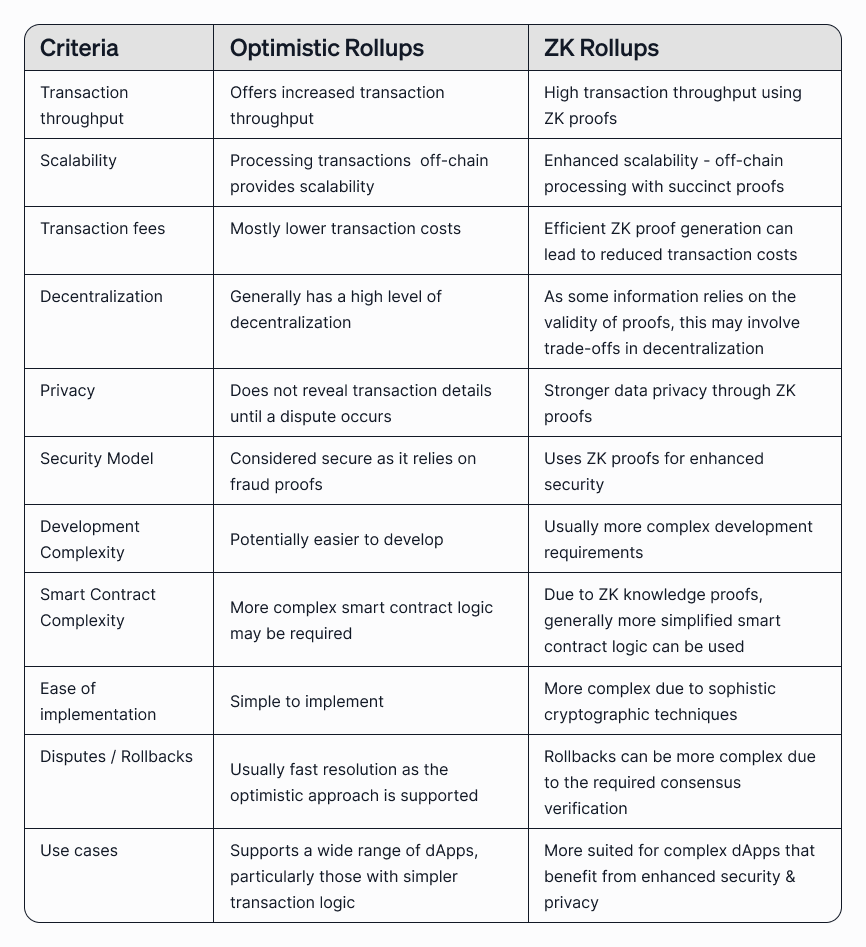
We have covered the two primary L2s that stand out as robust solutions. However, trade-offs exist between these 2 primary rollups.
For example, optimistic rollups may result in higher latencies as compared to ZK rollups. This is due to a time delay occurring between the off-chain processing and the final mainchain verification.
There is also a minimal chance that undetected fraudulent transactions might occur before they are contested.
Alternatively, ZK rollups require more complex cryptographic computations. These are generally more technically complex to implement. And they may have higher computational costs.
Moving ahead into 2025: Consumer-centric decentralization with modular blockchains
There is no doubt that layer-2 offers the scalability required for efficient dApp development. And as the demand for dApps continues to grow, this underlines the importance of layer-2 solutions.
Innovations like sovereign rollups, data availability layers, and consumer-focused layer-2 networks are ushering in the move towards a more flexible and user-centric Web3.
To succeed, the focus must shift to execution, integration, and delivering seamless experiences. While challenges like liquidity bridging and user education remain, the modular approach offers undeniable advantages.
The race to shape Web3’s future is on, and modular blockchain projects are in a favorable position to lead the charge.
Dive deeper into the unique features of each blockchain by learning about consumer chains and how they’re changing the outlook of Web3 builds by moving forward in this Track.