It brought about Cryptocurrency because people wanted to make money “better.” But the centralization of money was only the first issue blockchain attempted to solve.
Blockchain can bring improvement in countless areas of business, community, and culture, and music is one of them.

When traditional contracts no longer fulfill their purpose
Like in every industry, the music business is based on contracts. In one corner, you have the musicians, in the second corner, the audience willing to pay for it. Then there’s a third corner to the triangle: the intermediaries like labels, distributors, ticket masters, or streaming services. Unfortunately, the contracts – as we’ve heard from Marco – aren’t always fair, and the distribution of money – as we learned from Marcell – doesn’t always make sense.
In the past, the distributors functioned as gatekeepers as the strongest part of the contract. They naturally created a favorable deal, primarily for themselves. Who wouldn’t?
Now the times have changed. There are many new gates through which performing artists can reach their audiences. Musicians can become – and do become – one-stop-shops from the art to the business to the distribution.
The main issues with today’s contracts are:
- They are based on trust
- They slow down and complicate the payment process
- They add costs to the process
Then why not simply redraw the contracts and shift some revenue from the labels and streamers towards the musicians? The answer is simple: it’s not in the interest of those who control the interface between music creators and producers and consumers – the same party in the contract that gets the biggest share. The intermediaries have the power to set the conditions and even shut the musician out completely.
On top of that, there’s a technical issue. Music lives on the internet, which in its current state is basically a huge copy machine. With a little wittiness, anyone can copy anything.
For a musician to place their music online requires them to trust the distributor and the fans to respect their ownership and copyrights. Even if contracts were good, if the technology your music lives on does the opposite, they are worth as much as a random handshake with a stranger on the subway. We were all taught not to trust random strangers for a good reason.

Trust has been the basis for contracts for thousands of years. That worked well as long as the people who entered them knew each other. But strangers who make contracts need a neutral middleperson to make sure that trust isn’t breached. If that mediator functions as a duplicating machine, neither side can trust them.
Technology doesn’t require trust
You’re beginning to understand where this is going, right? Technology is the key. With blockchain technology, we’re no longer relying on trust, we have cryptography instead. You could call blockchain a “trust machine” because it functions as a substitute for trust in a traditional business setup. You’ll also hear the term “trustless” in this context.
The distributed ledger technology, in combination with cryptography, offers characteristics that make it possible:
- There isn’t one governing body with a self-interest in manipulating data.
- Records are immutable, meaning no one, not even the original creator, can change data in a closed block.
- Data is easily and autonomously verifiable.
Smart contracts and consensus mechanisms
Let’s take it a step further and add smart contracts to the list. A smart contract is a condition, or behavioral logic, included in the transaction on the blockchain. We are talking about a “if x then y” scenario. In music streaming, this could look something like “if this track gets streamed, then x amount of money gets released to artist Y”, or, “if a fan streams an artist’s track for the 50th time, then they get a voucher for a free ticket to the next concert”.
You can add information, such as copyright, metadata, or conditions to these little bundles of transactions called blocks and no one can change it, not even you. More and more blocks get added, but that will never change the information stored in them.
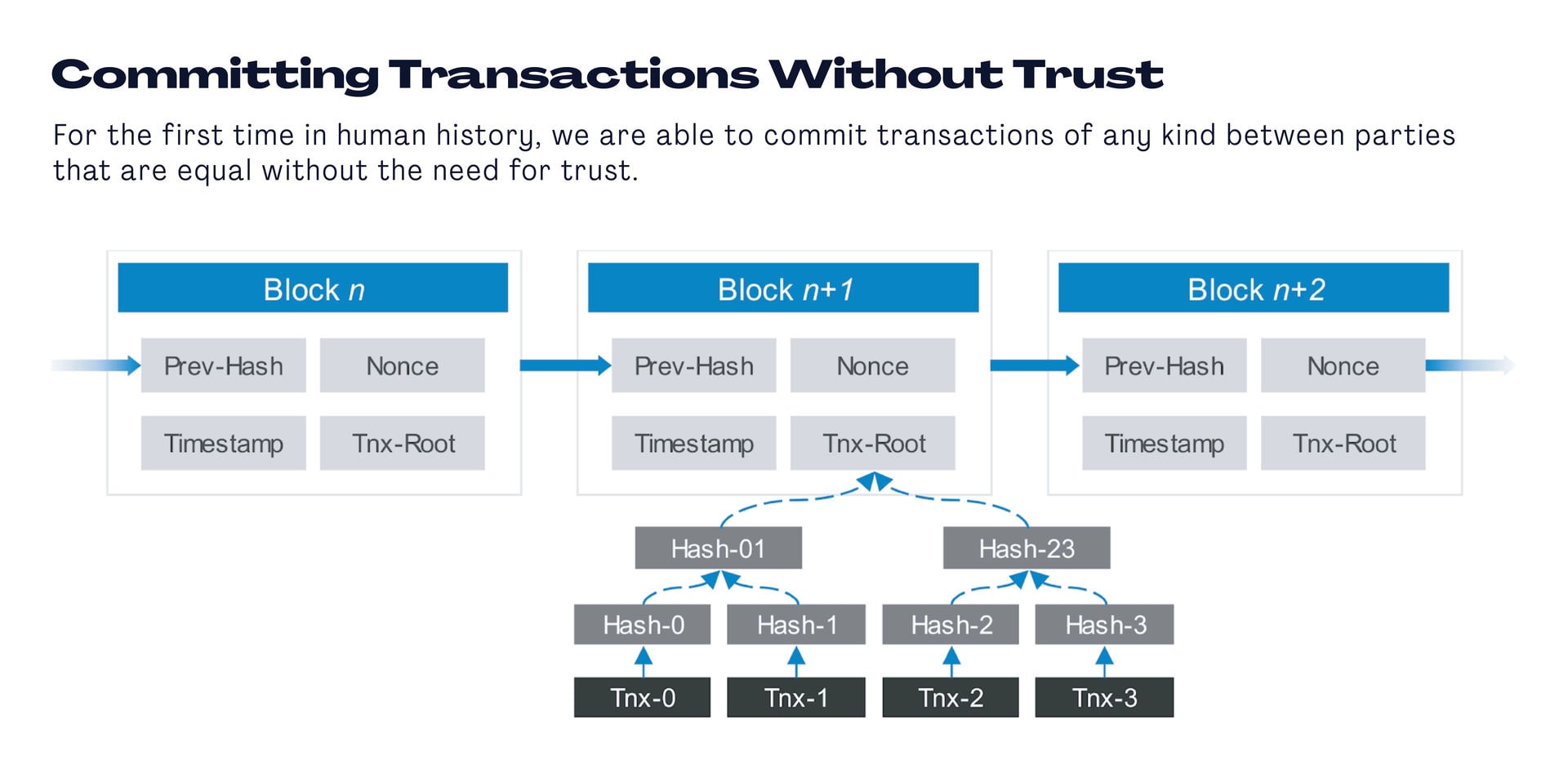
There’s really no limit to what you can do with this functionality – give out rewards, grant access or membership, let people vote, collect data – it’s up to your imagination. New things can pop up when you use such a distributed ledger on the internet.
That’s the beauty of blockchain. You can keep coming up with new ways of distributing music or interacting with your audience, the people who follow your work.
The blockchain works autonomously with no one in the middle who sets the rules on how to interact and what you can or can’t do (while grabbing a share of the money on the way). That’s not to say the system has no rules, there’s simply no “ruler”. Instead, blockchain uses consensus embedded in the algorithm. This consensus mechanism autonomously ensures that the rules are met, and that’s a game changer.
Now let’s sum up what blockchain can do for the music industry:
- Remove the middlemen
- Resolve the trust problem
- Enable direct contact between musician and fans
- Open new revenue streams
- Protect the ownership rights of creators

Examples of blockchain music apps
First up, our friends from Muzikie – creating a fair and fresh music streaming platform https://muzikie.com/

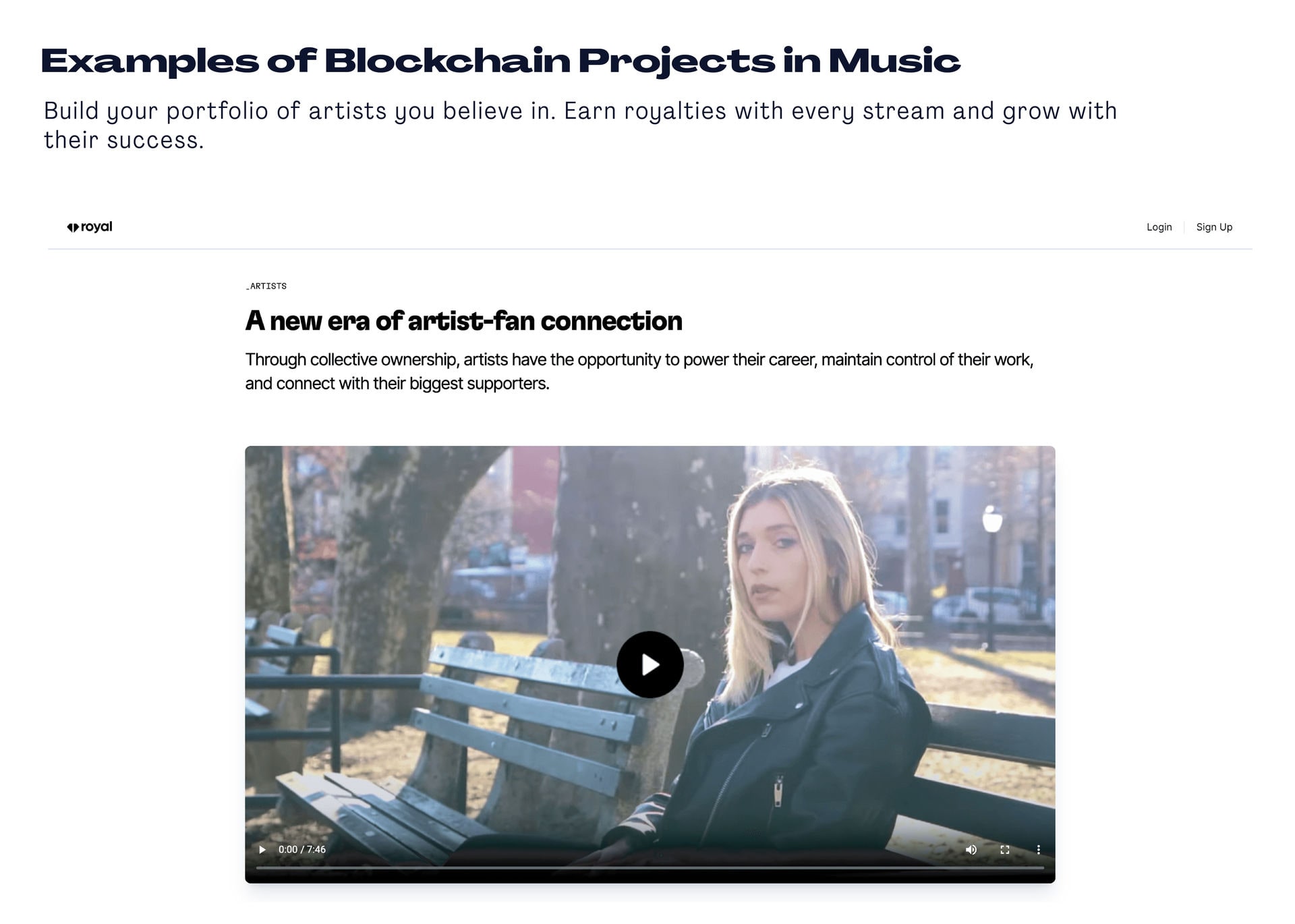
Another interesting platform is the Royal blockchain, where fans can build a portfolio of their favorite artists and earn royalties with every stream. Fans support their stars and grow with them. https://royal.io/
Openmusic Initiative is another way fans can directly support musicians. The open-source protocol identifies music rights and helps creators monetize their music. https://open-music.org/

When it comes to music rights, Blokur is also worth looking at. It connects the dots between rights holders, music creators, and music users. https://blokur.com/
Blockchain is already changing the music industry. This is just the beginning. You too, can jump on the creative train and enter the blockchain and music ecosystem – as a musician, a fan, or a builder.